Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products(PPCPs) from wastewater: A review
2
2016
... 微量有机污染物由于其愈发严重的污染现状受到了广泛关注〔1-2〕.许多微量有机污染物如药物和个人护理用品等都具有持久性及低浓度下的生态毒性.在对微量有机污染物降解去除时,研究者们发现其生物降解效果欠佳〔1, 3〕,污染物去除不完全.基于自由基的高级氧化工艺(Advanced oxidation process,AOPs)能够将难以降解的微量有机污染物有效降解转化为各种中间产物,并最终转变为CO2、H2O等产物〔4〕. ...
... 〔1, 3〕,污染物去除不完全.基于自由基的高级氧化工艺(Advanced oxidation process,AOPs)能够将难以降解的微量有机污染物有效降解转化为各种中间产物,并最终转变为CO2、H2O等产物〔4〕. ...
Fe-based catalysts for heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater
1
2017
... 微量有机污染物由于其愈发严重的污染现状受到了广泛关注〔1-2〕.许多微量有机污染物如药物和个人护理用品等都具有持久性及低浓度下的生态毒性.在对微量有机污染物降解去除时,研究者们发现其生物降解效果欠佳〔1, 3〕,污染物去除不完全.基于自由基的高级氧化工艺(Advanced oxidation process,AOPs)能够将难以降解的微量有机污染物有效降解转化为各种中间产物,并最终转变为CO2、H2O等产物〔4〕. ...
Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil
1
2014
... 微量有机污染物由于其愈发严重的污染现状受到了广泛关注〔1-2〕.许多微量有机污染物如药物和个人护理用品等都具有持久性及低浓度下的生态毒性.在对微量有机污染物降解去除时,研究者们发现其生物降解效果欠佳〔1, 3〕,污染物去除不完全.基于自由基的高级氧化工艺(Advanced oxidation process,AOPs)能够将难以降解的微量有机污染物有效降解转化为各种中间产物,并最终转变为CO2、H2O等产物〔4〕. ...
Removal of residual pharmaceuticals from aqueous systems by advanced oxidation processes
1
2009
... 微量有机污染物由于其愈发严重的污染现状受到了广泛关注〔1-2〕.许多微量有机污染物如药物和个人护理用品等都具有持久性及低浓度下的生态毒性.在对微量有机污染物降解去除时,研究者们发现其生物降解效果欠佳〔1, 3〕,污染物去除不完全.基于自由基的高级氧化工艺(Advanced oxidation process,AOPs)能够将难以降解的微量有机污染物有效降解转化为各种中间产物,并最终转变为CO2、H2O等产物〔4〕. ...
Irradiation treatment of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in water and wastewater: An overview
1
2016
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
Degradation of chlorotriazine pesticides by sulfate radicals and the influence of organic matter
1
2015
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
Degradation of bisphenol a using ozone/persulfate process: Kinetics and mechanism
1
2016
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
Oxidation of bisoprolol in heated persulfate/H2O systems: Kinetics and products
1
2012
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
Activation of persulfate(PS) and peroxymonosulfate(PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants
3
2018
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
... 〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation for the degradation of p-nitrophenol in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with CuFe2O4 magnetic nano-particles
1
2017
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
Reactions of phosphate radicals with organic-compounds
1
1977
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review
1
2010
... 常规高级氧化工艺主要依赖于HO·氧化降解污染物〔5〕.HO·是一种非选择性强氧化剂,可以破坏有机化合物的结构,使其转化为无机物.除了HO·外,研究人员注意到基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·-)的高级氧化技术也在降解微量有机污染物上表现出了突出优势〔6-7〕.基于SO4·-的高级氧化技术以过硫酸盐(Persulfate,PS)作为氧化剂,通过对氧化剂的活化产生具有高氧化性的SO4·-.与HO·相比,SO4·-具有高的氧化还原电位(2.5~3.1 V)〔8〕,在水中具有更长的维持时间〔9〕,能在更宽的pH范围内发挥作用,对环状结构的污染物去除更有针对性〔9-10〕,其氧化剂PS比产生HO·的氧化剂(如H2O2等)更易储存运输.在PS产生SO4·-时,往往会伴随产生HO·.SO4·-通过夺氢、双键加成和电子转移与有机分子发生反应〔11〕.SO4·-呈现亲电子性,与供电子基团的反应速率比与吸电子基团更快〔12〕. ...
Thermally activated persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene(TCE) and 1, 1, 1-trichloroethane(TCA) in aqueous systems and soil slurries
1
2003
... PS分为过氧一硫酸盐(Peroxymonosulfate,PMS)和过氧二硫酸盐(Peroxydisulfate,PDS).PMS为白色固体粉末,在pH为9时,PMS稳定性最差,其中HSO5-会有一半分解成SO52-,在实际应用中以白色三元盐(2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4)的形式使用.PDS为无色或白色晶体,具有高稳定性,溶解度为730 g/L〔13〕.实验中常使用的PDS是Na2S2O8和K2S2O8.PDS和PMS都是强氧化剂,氧化还原电位分别为2.01 V和1.82 V,在基于SO4·-的高级氧化工艺降解去除新兴污染物中都有应用〔14-15〕.PS能与污染物直接反应,但是反应速率低.为了提高反应速率,需要对PDS和PMS进行活化,产生高氧化性的自由基. ...
Efficient degradation of atrazine with porous sulfurized Fe2O3 as catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation
1
2019
... PS分为过氧一硫酸盐(Peroxymonosulfate,PMS)和过氧二硫酸盐(Peroxydisulfate,PDS).PMS为白色固体粉末,在pH为9时,PMS稳定性最差,其中HSO5-会有一半分解成SO52-,在实际应用中以白色三元盐(2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4)的形式使用.PDS为无色或白色晶体,具有高稳定性,溶解度为730 g/L〔13〕.实验中常使用的PDS是Na2S2O8和K2S2O8.PDS和PMS都是强氧化剂,氧化还原电位分别为2.01 V和1.82 V,在基于SO4·-的高级氧化工艺降解去除新兴污染物中都有应用〔14-15〕.PS能与污染物直接反应,但是反应速率低.为了提高反应速率,需要对PDS和PMS进行活化,产生高氧化性的自由基. ...
Molybdenum disulfide(MoS2): A versatile activator of both peroxymonosulfate and persulfate for the degradation of carbamazepine
1
2020
... PS分为过氧一硫酸盐(Peroxymonosulfate,PMS)和过氧二硫酸盐(Peroxydisulfate,PDS).PMS为白色固体粉末,在pH为9时,PMS稳定性最差,其中HSO5-会有一半分解成SO52-,在实际应用中以白色三元盐(2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4)的形式使用.PDS为无色或白色晶体,具有高稳定性,溶解度为730 g/L〔13〕.实验中常使用的PDS是Na2S2O8和K2S2O8.PDS和PMS都是强氧化剂,氧化还原电位分别为2.01 V和1.82 V,在基于SO4·-的高级氧化工艺降解去除新兴污染物中都有应用〔14-15〕.PS能与污染物直接反应,但是反应速率低.为了提高反应速率,需要对PDS和PMS进行活化,产生高氧化性的自由基. ...
Degradation kinetics and mechanism of beta-lactam antibiotics by the activation of H2O2 and Na2S2O8 under UV-254 nm irradiation
1
2014
... 活化PS产生自由基的部分途径见方程式(1)~(11)〔16-18〕. ...
Degradation of 1, 4-dioxane in water with heat-and Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation
0
2014
Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate
1
2009
... 活化PS产生自由基的部分途径见方程式(1)~(11)〔16-18〕. ...
Review on ultrasound assisted persulfate degradation of organic contaminants in wastewater: Influences, mechanisms and prospective
2
2019
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
... 超声与过渡金属联合活化,除了过渡金属和超声本身对PS的活化,还存在其他机理.超声活化由于空泡作用,会促进反应体系中的传质过程〔60〕,产生局部高温,存在部分热活化作用〔19〕.超声活化与过渡金属的协同作用主要是通过空泡作用实现的〔方程式(21)~(23),式中“)))”指超声处理〕. ...
Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review
1
2016
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Degradation of volatile organic compounds with thermally activated persulfate oxidation
1
2005
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Kinetic oxidation of antipyrine in heat-activated persulfate
1
2015
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Degradation and dechlorination of pentachlorophenol by microwave-activated persulfate
1
2015
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Degradation efficiencies of azo dye acid orange 7 by the interaction of heat, UV and anions with common oxidants: Persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide
1
2010
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Inactivation of water pathogens with solar photo-activated persulfate oxidation
1
2020
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Sono-activated persulfate oxidation of diclofenac: Degradation, kinetics, pathway and contribution of the different radicals involved
1
2018
... PDS和PMS中O—O的键能在140~213.3 kJ/mol的范围内.热活化、紫外活化、超声活化以及伽马射线活化等,主要是通过输入能量引起O—O键的裂变,从而生成SO4·-完成对PS的活化,其产生的优秀活化效果在部分综述中已经有所阐述〔9, 19-20〕.Kunchang Huang等〔21〕研究了59种挥发性有机化合物的热活化PDS降解,结果表明,反应温度是一个至关重要的因素,升高温度会有利于污染物的降解〔22-23〕.Shiying Yang等〔24〕的研究表明热活化对PDS有效,对PMS无效,其具体的机制还有待探究.紫外活化具有反应条件简单、无需调节pH、成本低等优点.L. C. Ferreira等〔25〕利用阳光照射活化PDS对水消毒,发现经照射后的水中大肠杆菌和粪肠球菌均被灭活,为水低成本回收提供了参考.超声波在水溶液中会引起剧烈的湍流,增强传质,也有利于污染物的去除.J. M. Monteagudo等〔26〕通过US/PDS去除双氯芬酸,240 min后去除率为98%,其机理是超声波产生了空化气泡以此促进了自由基产生. ...
Impact of peroxydisulfate in the presence of zero valent iron on the oxidation of cyclohexanoic acid and naphthenic acids from oil sands process-affected water
1
2012
... 热活化PS需要大量的能量,在实际大规模应用中并不适合.此外,随着温度的升高,SO4·-和潜在清除剂(例如氯离子和碳酸氢根离子)的反应速率也会增加,进而影响污染物的去除效率〔27〕.与热活化类似,超声活化的本质也是能量的输入,其经济成本压力是限制其应用的关键障碍.而UV的穿透能力弱,在大水体中应用时也会受到限制. ...
Insights into heterogeneous catalysis of persulfate activation on dimensional-structured nanocarbons
1
2015
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
Activated carbon and carbon black catalyzed transformation of aqueous ozone into OH-radicals
1
1998
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
Exploring the role of persulfate in the activation process: Radical precursor versus electron acceptor
2
2017
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
... 此外,经过文献调研,活化方式本身对污染物有一定去除作用,但是这种去除作用大小根据污染物和活化方式而变.例如,Yingying Fu等〔47〕通过UV/PDS降解人工甜味剂时发现,UV在安赛蜜的降解中有51%的贡献率,这表明活化方式UV本身对污染物就有相当的降解作用.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕用太阳光、加热等方式活化PS去除水中的病原菌(大肠杆菌),是由于适当的温度和紫外光对细菌具备一定的杀伤作用.而E. T. Yun等〔30〕在用纳米零价铁和单壁碳纳米管活化PDS去除双酚A等7种有机底物时,发现这两种活化方式本身也能去除污染物,但是去除率只有5%~10%.此外,对于一些具有特殊结构的污染物,针对污染物的结构特性选用活化方式会事半功倍.例如全氟烷基物质在超声波中会有效减少长度,变得更易降解,Yongjia Lei等〔49〕通过US/PDS降解全氟烷基物质,在6 h后脱氟率达到100%.再比如钴氰基络合物具有光敏性,活化方式选择UV会更易降解,S. F. Castilla-Acevedo等〔50〕通过UV/PDS降解钴氰基络合物,其降解率达到99%. ...
Determining the key factors of nonradical pathway in activation of persulfate by metalbiochar nanocomposites for bisphenol a degradation
1
2020
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants
1
2004
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
Cobalt-catalyzed sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation: A review on heterogeneous catalysts and applications
1
2016
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
Sulfate radical-based ferrous-peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for pcbs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems
1
2009
... 各种碳材料、过渡金属异质活化剂、过渡金属氧化物等对PS也有活化作用,这些材料在PS活化中类似于催化剂,能够促进自由基产生.碳材料活化PS有两种机制,一种机制是多壁碳纳米管缺陷边缘sp2共价碳网络和含氧官能团(污染物)进行氧化还原循环,使电子转移到PS上产生自由基〔28〕;另一种机制是电子从碳材料中抽出,然后转移给PS〔29〕.E. T. Yun等〔30〕研究了多壁碳纳米管在活化PS过程中的机理,发现在去除污染物过程中碳纳米管不与PS发生直接反应,而是将电子从污染物转移到PS.而Haoyu Luo等〔31〕在研究含有芳族结构的生物炭活化PS降解双酚A时发现,反应过程中生物炭和PS先形成反应性中间体,发生电子转移,再将双酚A降解.在均相的金属离子和氧化物中,银离子(Ag+)活化PDS最有效〔32〕,而钴离子(Co2+)活化PMS性能最好〔33〕.过渡金属异质活化剂通常以不同过渡金属氧化物结合的形式出现,利用不同过渡金属氧化还原电位的差异实现部分过渡金属还原,进而促进PS分解.与其他过渡金属相比,铁具有环境友好、相对无毒、成本低等优点,是研究最多的过渡金属〔34〕.过渡金属对PS的活化原理是通过过渡金属的电子传递实现的,即过渡金属自身氧化,将电子传递给PS产生自由基. ...
Degradation of pesticide thiamethoxam by heat-activated and ultrasound-activated persulfate: Effect of key operating parameters and the water matrix
1
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
Treatment of wastewater containing 2-methoxyphenol by persulfate with thermal and alkali synergistic activation: Kinetics and mechanism
3
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
... 在其他非金属活化类型的联合中,通常热的参与可增强能量输入,促进自由基产生.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕研究了铁微粒/UV/热联合活化PDS对微污染物的降解效果及对细菌、病毒的灭杀效果,其中UV与热的协同作用较低,但是通过能量输入,处理效果较好.Zhihui Huang等〔36〕在热碱联合活化PDS去除废水中的2-甲氧基苯酚时发现,在pH=12时,联合系统产生大量自由基,导致自由基猝灭剂失效.Xiaoguang Duan〔76〕合成氮掺杂的碳纳米管(NSWCANT)作为非金属催化剂活化PDS,发现在55~75 ℃段,热/碳耦合系统的协同作用明显,可以显著降低PDS活化能,但是具体的协同原理尚未探明. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Enhanced removal of emerging contaminants using persulfate activated by UV and premagnetized Fe0
3
2019
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Degradation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole by biochar-activated persulfate: Factors affecting the activation and degradation processes
2
2018
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by ag doped BiFeO3 composites for tetracycline degradation
1
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
Synergistic degradation of acid blue 113 dye in a thermally activated persulfate(TAP)/ZnO-GAC oxidation system: Degradation pathway and application for real textile wastewater
0
2020
Synergistic effect of persulfate and g-C3N4 under simulated solar light irradiation: Implication for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole
1
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
Degradation of diazinon pesticide using catalyzed persulfate with Fe3O4@MOF-2 nanocomposite under ultrasound irradiation
2
2019
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
... 超声与零价金属(如零价铁、零价铜)联合活化PS时,会对零价金属的表面产生腐蚀作用,促进能够活化PS的金属离子产生〔方程式(21)〕〔61〕;超声与金属氧化物联合活化时,会腐蚀氧化物表面促进金属离子的释放,并且对金属离子活化PS的反应有促进作用〔方程式(22)、(23)〕〔62〕.此外,超声会清洁金属表面由于反应产生的惰性物质(高价氧化物等),促使金属表面不断更新,加快金属离子的产生〔42, 63〕,保证PS能够高效生成自由基.Yixiong Pang等〔63〕用超声辅助粉末零价铁活化PMS降解罗丹明B,超声促进了零价铁产生铁离子,将零价铁/PMS体系对罗丹明B的去除率从35%提高到近乎100%. ...
Mechanisms of electro-assisted persulfate/nano-Fe0 oxidation process: Roles of redox mediation by dissolved Fe
1
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
Reduced graphene oxide-supported metal organic framework as a synergistic catalyst for enhanced performance on persulfate induced degradation of trichlorophenol
1
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
Understanding the synergetic effect from foreign metals in bimetallic oxides for pms activation: A common strategy to increase the stoichiometric efficiency of oxidants
3
2020
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
... 不同过渡金属氧化物的有机组合,多是以异质催化剂的形式出现,这样可以克服均相情况下金属离子难以回收、金属离子易受污水pH影响等缺陷.过渡金属联合活化体现了过渡金属之间的协同作用,可实现PS比单纯物理混合更好的活化效果,提高对相应污染物的去除率和矿化率〔45, 51〕.这种协同作用,是通过不同金属间的电子转移,促进某种金属离子不断再生实现的,其原理如方程式(16)~(20)所示. ...
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by using ferroferric oxide supported on carbon/UV/ US system: A new approach into catalytic degradation of bisphenol A
2
2018
... 热活化、超声活化、紫外活化、过渡金属活化、碳材料活化等活化方式已经展现出与其他活化方式联合的趋势,比如热活化和超声活化联合〔35〕、热活化和碱活化联合〔36〕、紫外活化和过渡金属活化联合〔37〕、生物炭与超声联合〔38〕等.经过联合后,以体系内一种活化条件为主体,其他活化条件作为促进成分〔39-42〕使PS产生自由基的能力得到增强〔41, 43-44〕.联合活化在研究中被证实了协同效应的存在〔45-46〕,即联合活化可表现超越单一活化简单加和的污染物去除效果. ...
... 碳材料具有大比表面积、高孔体积等优点,在与过渡金属的联合活化中,协同效应主要是通过碳材料的良电子传导性能实现的.碳材料的良电子传导性,可以加快过渡金属与PS之间的电子传递,促进活化PS.此外,碳材料通常会掺杂N等元素改变材料性能,这些掺杂的元素与过渡金属可能也会产生相互作用增强对PS的活化.Zhifei Ma等〔71〕联合零价铁和活性炭活化PDS,发现活性炭对电子的传导促进了Fe2+的产生和PDS的活化.A. Takdastan等〔46〕将Fe3O4负载在活性炭上合成材料MNPs@C,发现材料表面存在快速电子转移,可促进PMS活化.Zhi Jiang等〔72〕合成了包裹有Co3O4的氮掺杂碳纳米管,发现合成材料中Co—N键具有强吸电子能力,且氮掺杂碳纳米管和Co3O4的异质表面利于电子转移,促进了PS的电子传递活化. ...
Removal of artificial sweeteners using UV/persulfate: Radical-based degradation kinetic model in wastewater, pathways and toxicity
1
2019
... 此外,经过文献调研,活化方式本身对污染物有一定去除作用,但是这种去除作用大小根据污染物和活化方式而变.例如,Yingying Fu等〔47〕通过UV/PDS降解人工甜味剂时发现,UV在安赛蜜的降解中有51%的贡献率,这表明活化方式UV本身对污染物就有相当的降解作用.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕用太阳光、加热等方式活化PS去除水中的病原菌(大肠杆菌),是由于适当的温度和紫外光对细菌具备一定的杀伤作用.而E. T. Yun等〔30〕在用纳米零价铁和单壁碳纳米管活化PDS去除双酚A等7种有机底物时,发现这两种活化方式本身也能去除污染物,但是去除率只有5%~10%.此外,对于一些具有特殊结构的污染物,针对污染物的结构特性选用活化方式会事半功倍.例如全氟烷基物质在超声波中会有效减少长度,变得更易降解,Yongjia Lei等〔49〕通过US/PDS降解全氟烷基物质,在6 h后脱氟率达到100%.再比如钴氰基络合物具有光敏性,活化方式选择UV会更易降解,S. F. Castilla-Acevedo等〔50〕通过UV/PDS降解钴氰基络合物,其降解率达到99%. ...
Effect of um Fe addition, mild heat and solar UV on sulfate radical-mediated inactivation of bacteria, viruses, and micropollutant degradation in water
4
2018
... 此外,经过文献调研,活化方式本身对污染物有一定去除作用,但是这种去除作用大小根据污染物和活化方式而变.例如,Yingying Fu等〔47〕通过UV/PDS降解人工甜味剂时发现,UV在安赛蜜的降解中有51%的贡献率,这表明活化方式UV本身对污染物就有相当的降解作用.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕用太阳光、加热等方式活化PS去除水中的病原菌(大肠杆菌),是由于适当的温度和紫外光对细菌具备一定的杀伤作用.而E. T. Yun等〔30〕在用纳米零价铁和单壁碳纳米管活化PDS去除双酚A等7种有机底物时,发现这两种活化方式本身也能去除污染物,但是去除率只有5%~10%.此外,对于一些具有特殊结构的污染物,针对污染物的结构特性选用活化方式会事半功倍.例如全氟烷基物质在超声波中会有效减少长度,变得更易降解,Yongjia Lei等〔49〕通过US/PDS降解全氟烷基物质,在6 h后脱氟率达到100%.再比如钴氰基络合物具有光敏性,活化方式选择UV会更易降解,S. F. Castilla-Acevedo等〔50〕通过UV/PDS降解钴氰基络合物,其降解率达到99%. ...
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
... 热与过渡金属的联合比单独的活化效果表现更好,但是这种效率改善是由于各自的单纯加和还是存在协同效应缺乏探究.Yangxian Liu等〔69〕在研究US/热/Fe2+/PDS体系处理烟道气中的SO2和NO时发现整个体系具备协同效应.A. Aher等〔70〕发现,在不存在和存在Fe2+的情况下,PDS热解的活化能分别为140.16和75.31 kJ/mol,说明过渡金属可能以通过降低活化能的形式与热协同活化PDS.而M. Marjanovic等〔48〕在研究低剂量铁、热和紫外联合活化PDS对细菌灭活时,通过对协同指数计算,发现在40 ℃时,Fe2+和热的联合活化只有单独活化方式的简单加和,没有表现出协同作用.因此说,热作为一种直接的能量输入,与过渡金属之间的协同效应尚不明确. ...
... 在其他非金属活化类型的联合中,通常热的参与可增强能量输入,促进自由基产生.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕研究了铁微粒/UV/热联合活化PDS对微污染物的降解效果及对细菌、病毒的灭杀效果,其中UV与热的协同作用较低,但是通过能量输入,处理效果较好.Zhihui Huang等〔36〕在热碱联合活化PDS去除废水中的2-甲氧基苯酚时发现,在pH=12时,联合系统产生大量自由基,导致自由基猝灭剂失效.Xiaoguang Duan〔76〕合成氮掺杂的碳纳米管(NSWCANT)作为非金属催化剂活化PDS,发现在55~75 ℃段,热/碳耦合系统的协同作用明显,可以显著降低PDS活化能,但是具体的协同原理尚未探明. ...
Synergistic degradation of pfas in water and soil by dual-frequency ultrasonic activated persulfate
1
2020
... 此外,经过文献调研,活化方式本身对污染物有一定去除作用,但是这种去除作用大小根据污染物和活化方式而变.例如,Yingying Fu等〔47〕通过UV/PDS降解人工甜味剂时发现,UV在安赛蜜的降解中有51%的贡献率,这表明活化方式UV本身对污染物就有相当的降解作用.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕用太阳光、加热等方式活化PS去除水中的病原菌(大肠杆菌),是由于适当的温度和紫外光对细菌具备一定的杀伤作用.而E. T. Yun等〔30〕在用纳米零价铁和单壁碳纳米管活化PDS去除双酚A等7种有机底物时,发现这两种活化方式本身也能去除污染物,但是去除率只有5%~10%.此外,对于一些具有特殊结构的污染物,针对污染物的结构特性选用活化方式会事半功倍.例如全氟烷基物质在超声波中会有效减少长度,变得更易降解,Yongjia Lei等〔49〕通过US/PDS降解全氟烷基物质,在6 h后脱氟率达到100%.再比如钴氰基络合物具有光敏性,活化方式选择UV会更易降解,S. F. Castilla-Acevedo等〔50〕通过UV/PDS降解钴氰基络合物,其降解率达到99%. ...
Ultraviolet light-mediated activation of persulfate for the degradation of cobalt cyanocomplexes
1
2020
... 此外,经过文献调研,活化方式本身对污染物有一定去除作用,但是这种去除作用大小根据污染物和活化方式而变.例如,Yingying Fu等〔47〕通过UV/PDS降解人工甜味剂时发现,UV在安赛蜜的降解中有51%的贡献率,这表明活化方式UV本身对污染物就有相当的降解作用.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕用太阳光、加热等方式活化PS去除水中的病原菌(大肠杆菌),是由于适当的温度和紫外光对细菌具备一定的杀伤作用.而E. T. Yun等〔30〕在用纳米零价铁和单壁碳纳米管活化PDS去除双酚A等7种有机底物时,发现这两种活化方式本身也能去除污染物,但是去除率只有5%~10%.此外,对于一些具有特殊结构的污染物,针对污染物的结构特性选用活化方式会事半功倍.例如全氟烷基物质在超声波中会有效减少长度,变得更易降解,Yongjia Lei等〔49〕通过US/PDS降解全氟烷基物质,在6 h后脱氟率达到100%.再比如钴氰基络合物具有光敏性,活化方式选择UV会更易降解,S. F. Castilla-Acevedo等〔50〕通过UV/PDS降解钴氰基络合物,其降解率达到99%. ...
MnCeOx with high efficiency and stability for activating persulfate to degrade AO7 and ofloxacin
1
2020
... 不同过渡金属氧化物的有机组合,多是以异质催化剂的形式出现,这样可以克服均相情况下金属离子难以回收、金属离子易受污水pH影响等缺陷.过渡金属联合活化体现了过渡金属之间的协同作用,可实现PS比单纯物理混合更好的活化效果,提高对相应污染物的去除率和矿化率〔45, 51〕.这种协同作用,是通过不同金属间的电子转移,促进某种金属离子不断再生实现的,其原理如方程式(16)~(20)所示. ...
Heterogeneous degradation of organic pollutants by persulfate activated by CuO-Fe3O4: Mechanism, stability, and effects of pH and bicarbonate ions
2
2015
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
... 〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
Fe(Ⅱ)-promoted activation of peroxymonosulfate by molybdenum disulfide for effective degradation of Acetaminophen
1
2020
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
Synergistic activation of peroxymonosulfate and persulfate by ferrous ion and molybdenum disulfide for pollutant degradation: Theoretical and experimental studies
2
2020
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Oxidation of bisphenol a by persulfate via Fe3O4-alpha-MnO2 nanoflower-like catalyst: Mechanism and efficiency
2
2019
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
Re-utilization of spent Cu2+-immobilized MgMn-layered double hydroxide for efficient sulfamethoxazole degradation: Performance and metals synergy
1
2020
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
Bimetallic Fe/ Ti-based metal-organic framework for persulfate-assisted visible light photocatalytic degradation of orange Ⅱ
2
2018
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
An efficient Cuogamma Fe2O3 composite activates persulfate for organic pollutants removal: Performance, advantages and mechanism
1
2020
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
Sulfur-doped copper-cobalt bimetallic oxides with abundant Cu(Ⅰ): A novel peroxymonosulfate activator for chloramphenicol degradation
1
2019
... 方程式(16)~(20)中Ma通常是指能够表现出更好活化性能的金属,Mb指能够促进Ma还原的金属.联合后的活化过程中存在各过渡金属对过硫酸盐的活化〔方程式(16)~(19)〕,但是这并不能展示出协同效应.方程式(20)通常发生在合成的异质活化剂表面,反应能够促进Man的不断再生,更利于PS裂键产生SO4·-,这是过渡金属实现协同活化作用的关键.Lei Yang等〔52〕制备了磁性CuO-Fe3O4活化剂活化PDS对苯酚进行降解,活化剂表面的Fe2+持续将活化PDS过程中生成的Cu3+还原为Cu2+.Xinquan Zhou等〔45〕研究了双金属氧化物中加入外来金属时对PMS活化的协同作用,发现Co与Cu之间通过电子传递存在协同效应,相比Co与其它过渡金属如Fe、Mn等更显著.除了前述的Cu与Fe、Cu与Co之间的电子转移,还存在Mo与Fe〔53-54〕、Fe和Mn〔55〕、Cu和Mn〔56〕、Fe和Ti〔57〕等不同过渡金属对的搭配.这种搭配有赖于组合的两种过渡金属的反应性能,反应的难易程度取决于反应的两种过渡金属各自氧化还原电位的差异〔52, 58〕.除此之外,在过渡金属的组合中,Cheng Chen等〔59〕添加了非金属元素S用于辅助金属还原,取得了较好的效果,其机理在于S改善了原本活化剂的结构,并且通过自身氧化辅助了过渡金属还原. ...
Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron(nZVI) for the propranolol degradation in water
1
2018
... 超声与过渡金属联合活化,除了过渡金属和超声本身对PS的活化,还存在其他机理.超声活化由于空泡作用,会促进反应体系中的传质过程〔60〕,产生局部高温,存在部分热活化作用〔19〕.超声活化与过渡金属的协同作用主要是通过空泡作用实现的〔方程式(21)~(23),式中“)))”指超声处理〕. ...
Degradation of sulfamethazine by persulfate activated with nanosized zero-valent copper in combination with ultrasonic irradiation
2
2020
... 超声与零价金属(如零价铁、零价铜)联合活化PS时,会对零价金属的表面产生腐蚀作用,促进能够活化PS的金属离子产生〔方程式(21)〕〔61〕;超声与金属氧化物联合活化时,会腐蚀氧化物表面促进金属离子的释放,并且对金属离子活化PS的反应有促进作用〔方程式(22)、(23)〕〔62〕.此外,超声会清洁金属表面由于反应产生的惰性物质(高价氧化物等),促使金属表面不断更新,加快金属离子的产生〔42, 63〕,保证PS能够高效生成自由基.Yixiong Pang等〔63〕用超声辅助粉末零价铁活化PMS降解罗丹明B,超声促进了零价铁产生铁离子,将零价铁/PMS体系对罗丹明B的去除率从35%提高到近乎100%. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: A review
1
2020
... 超声与零价金属(如零价铁、零价铜)联合活化PS时,会对零价金属的表面产生腐蚀作用,促进能够活化PS的金属离子产生〔方程式(21)〕〔61〕;超声与金属氧化物联合活化时,会腐蚀氧化物表面促进金属离子的释放,并且对金属离子活化PS的反应有促进作用〔方程式(22)、(23)〕〔62〕.此外,超声会清洁金属表面由于反应产生的惰性物质(高价氧化物等),促使金属表面不断更新,加快金属离子的产生〔42, 63〕,保证PS能够高效生成自由基.Yixiong Pang等〔63〕用超声辅助粉末零价铁活化PMS降解罗丹明B,超声促进了零价铁产生铁离子,将零价铁/PMS体系对罗丹明B的去除率从35%提高到近乎100%. ...
Ultrasound assisted zero valent iron corrosion for peroxymonosulfate activation for Rhodamine-B degradation
2
2019
... 超声与零价金属(如零价铁、零价铜)联合活化PS时,会对零价金属的表面产生腐蚀作用,促进能够活化PS的金属离子产生〔方程式(21)〕〔61〕;超声与金属氧化物联合活化时,会腐蚀氧化物表面促进金属离子的释放,并且对金属离子活化PS的反应有促进作用〔方程式(22)、(23)〕〔62〕.此外,超声会清洁金属表面由于反应产生的惰性物质(高价氧化物等),促使金属表面不断更新,加快金属离子的产生〔42, 63〕,保证PS能够高效生成自由基.Yixiong Pang等〔63〕用超声辅助粉末零价铁活化PMS降解罗丹明B,超声促进了零价铁产生铁离子,将零价铁/PMS体系对罗丹明B的去除率从35%提高到近乎100%. ...
... 〔63〕用超声辅助粉末零价铁活化PMS降解罗丹明B,超声促进了零价铁产生铁离子,将零价铁/PMS体系对罗丹明B的去除率从35%提高到近乎100%. ...
Photo-fenton-like degradation of bisphenol A by persulfate and solar irradiation
2
2019
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
... , 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
Sonophotocatalytic treatment of AB113 dye and real textile wastewater using ZnO/persulfate: Modeling by response surface methodology and artificial neural network
1
2020
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
Treatment of persistent organic pollutants in wastewater using hydrodynamic cavitation in synergy with advanced oxidation process
1
2018
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
Transition metal/UV-based advanced oxidation technologies for water decontamination
1
2004
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
Copper phosphide and persulfate salt: A novel catalytic system for the degradation of aqueous phase micro-contaminants
1
2019
... 过渡金属与UV联合时的协同活化机理有两种.一是UV促进金属离子的还原,许多过渡金属如Fe〔64〕、Mn〔55〕、Ti〔57〕等都会在与UV的联合过程中发生还原,促进活化PS〔方程式(24)〕〔48, 64〕.二是UV与半导体催化剂联合,产生光生电子活化PS.这主要是对于某些具备光催化剂作用的过渡金属化合物如TiO2、SeO2、ZnO等〔65〕,在与UV联合活化时,会吸收大于其带隙的UV辐射,进而产生电子-空穴对,产生的电子会利用过量能量来获得从价带到导带的激发从而活化PS,只留下正空穴〔66〕.G. P. Anipsitakis等〔67〕发现UV/Fe2+/PS在降解2,4-二氯苯酚时,Fe(Ⅲ)与有机酸络合后的产物会吸收UV反应再生Fe2+,促进活化PDS.C. Alexopoulou等〔68〕发现UV与Cu3P联合活化PS降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑时具有协同效应,其原理是在UV辐射下,Cu3P充当了一种电子介体,通过促进形成SO4·-加速电子转移过程. ...
Simultaneous absorption of SO2 and NO from flue gas using ultrasound/Fe2+/heat coactivated persulfate system
1
2018
... 热与过渡金属的联合比单独的活化效果表现更好,但是这种效率改善是由于各自的单纯加和还是存在协同效应缺乏探究.Yangxian Liu等〔69〕在研究US/热/Fe2+/PDS体系处理烟道气中的SO2和NO时发现整个体系具备协同效应.A. Aher等〔70〕发现,在不存在和存在Fe2+的情况下,PDS热解的活化能分别为140.16和75.31 kJ/mol,说明过渡金属可能以通过降低活化能的形式与热协同活化PDS.而M. Marjanovic等〔48〕在研究低剂量铁、热和紫外联合活化PDS对细菌灭活时,通过对协同指数计算,发现在40 ℃时,Fe2+和热的联合活化只有单独活化方式的简单加和,没有表现出协同作用.因此说,热作为一种直接的能量输入,与过渡金属之间的协同效应尚不明确. ...
Naphthenic acids removal from high tds produced water by persulfate mediated iron oxide functionalized catalytic membrane, and by nanofiltration
1
2017
... 热与过渡金属的联合比单独的活化效果表现更好,但是这种效率改善是由于各自的单纯加和还是存在协同效应缺乏探究.Yangxian Liu等〔69〕在研究US/热/Fe2+/PDS体系处理烟道气中的SO2和NO时发现整个体系具备协同效应.A. Aher等〔70〕发现,在不存在和存在Fe2+的情况下,PDS热解的活化能分别为140.16和75.31 kJ/mol,说明过渡金属可能以通过降低活化能的形式与热协同活化PDS.而M. Marjanovic等〔48〕在研究低剂量铁、热和紫外联合活化PDS对细菌灭活时,通过对协同指数计算,发现在40 ℃时,Fe2+和热的联合活化只有单独活化方式的简单加和,没有表现出协同作用.因此说,热作为一种直接的能量输入,与过渡金属之间的协同效应尚不明确. ...
Enhanced degradation of 2, 4-dinitrotoluene in groundwater by persulfate activated using iron-carbon micro-electrolysis
1
2017
... 碳材料具有大比表面积、高孔体积等优点,在与过渡金属的联合活化中,协同效应主要是通过碳材料的良电子传导性能实现的.碳材料的良电子传导性,可以加快过渡金属与PS之间的电子传递,促进活化PS.此外,碳材料通常会掺杂N等元素改变材料性能,这些掺杂的元素与过渡金属可能也会产生相互作用增强对PS的活化.Zhifei Ma等〔71〕联合零价铁和活性炭活化PDS,发现活性炭对电子的传导促进了Fe2+的产生和PDS的活化.A. Takdastan等〔46〕将Fe3O4负载在活性炭上合成材料MNPs@C,发现材料表面存在快速电子转移,可促进PMS活化.Zhi Jiang等〔72〕合成了包裹有Co3O4的氮掺杂碳纳米管,发现合成材料中Co—N键具有强吸电子能力,且氮掺杂碳纳米管和Co3O4的异质表面利于电子转移,促进了PS的电子传递活化. ...
Strong synergistic effect of Co3O4 encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes on the nonradical-dominated persulfate activation
1
2020
... 碳材料具有大比表面积、高孔体积等优点,在与过渡金属的联合活化中,协同效应主要是通过碳材料的良电子传导性能实现的.碳材料的良电子传导性,可以加快过渡金属与PS之间的电子传递,促进活化PS.此外,碳材料通常会掺杂N等元素改变材料性能,这些掺杂的元素与过渡金属可能也会产生相互作用增强对PS的活化.Zhifei Ma等〔71〕联合零价铁和活性炭活化PDS,发现活性炭对电子的传导促进了Fe2+的产生和PDS的活化.A. Takdastan等〔46〕将Fe3O4负载在活性炭上合成材料MNPs@C,发现材料表面存在快速电子转移,可促进PMS活化.Zhi Jiang等〔72〕合成了包裹有Co3O4的氮掺杂碳纳米管,发现合成材料中Co—N键具有强吸电子能力,且氮掺杂碳纳米管和Co3O4的异质表面利于电子转移,促进了PS的电子传递活化. ...
Investigation of the synergism of hybrid advanced oxidation processes with an oxidation agent to degrade three dyes
1
2017
... 紫外、超声、热以及非金属催化剂之间的联合活化也有部分研究.其中,紫外和超声联合活化的研究较多.紫外和超声联合活化时表现出的协同效应,一方面来源于对PS中自由基产率的提高,如A. Sharfalddin等〔73〕联合超声、紫外活化PDS对染料罗丹明B进行降解,发现超声和紫外的协同提高了自由基的产率;另一方面紫外光的存在能够使一部分污染物光解,配合超声产生的气蚀气泡能够增强传质,提高污染物的矿化率〔74〕.但并非所有情况下,联合活化都能表现出协同效应,如S. Chakma等〔75〕在另一项研究中发现,超声和紫外在联合活化PDS降解染料偶氮红霉素时得到的染料降解和矿化几乎等于使用单独活化时的总和,表现出低程度的协同作用. ...
Kinetic modeling and synergy quantification in sono and photooxidative treatment of simulated dyehouse effluent
1
2012
... 紫外、超声、热以及非金属催化剂之间的联合活化也有部分研究.其中,紫外和超声联合活化的研究较多.紫外和超声联合活化时表现出的协同效应,一方面来源于对PS中自由基产率的提高,如A. Sharfalddin等〔73〕联合超声、紫外活化PDS对染料罗丹明B进行降解,发现超声和紫外的协同提高了自由基的产率;另一方面紫外光的存在能够使一部分污染物光解,配合超声产生的气蚀气泡能够增强传质,提高污染物的矿化率〔74〕.但并非所有情况下,联合活化都能表现出协同效应,如S. Chakma等〔75〕在另一项研究中发现,超声和紫外在联合活化PDS降解染料偶氮红霉素时得到的染料降解和矿化几乎等于使用单独活化时的总和,表现出低程度的协同作用. ...
Mechanistic investigations in sono-hybrid (ultrasound/Fe2+/UVC) techniques of persulfate activation for degradation of azorubine
1
2017
... 紫外、超声、热以及非金属催化剂之间的联合活化也有部分研究.其中,紫外和超声联合活化的研究较多.紫外和超声联合活化时表现出的协同效应,一方面来源于对PS中自由基产率的提高,如A. Sharfalddin等〔73〕联合超声、紫外活化PDS对染料罗丹明B进行降解,发现超声和紫外的协同提高了自由基的产率;另一方面紫外光的存在能够使一部分污染物光解,配合超声产生的气蚀气泡能够增强传质,提高污染物的矿化率〔74〕.但并非所有情况下,联合活化都能表现出协同效应,如S. Chakma等〔75〕在另一项研究中发现,超声和紫外在联合活化PDS降解染料偶氮红霉素时得到的染料降解和矿化几乎等于使用单独活化时的总和,表现出低程度的协同作用. ...
Synergy of carbocatalytic and heat activation of persulfate for evolution of reactive radicals toward metal-free oxidation
1
2019
... 在其他非金属活化类型的联合中,通常热的参与可增强能量输入,促进自由基产生.M. Marjanovic等〔48〕研究了铁微粒/UV/热联合活化PDS对微污染物的降解效果及对细菌、病毒的灭杀效果,其中UV与热的协同作用较低,但是通过能量输入,处理效果较好.Zhihui Huang等〔36〕在热碱联合活化PDS去除废水中的2-甲氧基苯酚时发现,在pH=12时,联合系统产生大量自由基,导致自由基猝灭剂失效.Xiaoguang Duan〔76〕合成氮掺杂的碳纳米管(NSWCANT)作为非金属催化剂活化PDS,发现在55~75 ℃段,热/碳耦合系统的协同作用明显,可以显著降低PDS活化能,但是具体的协同原理尚未探明. ...
Ultrasound assisted photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac in an aqueous environment
1
2010
... 联合活化涉及到不同活化方式的耦合,这种耦合是否具有协同效应,可用协同指数(Synergy index,S)进行衡量〔77〕.伪一级动力学模型被广泛应用于描述常规和新型污染物的去除,其动力学方程式如式(25)所示. ...
Visible-light-driven sonophotocatalysis and peroxymonosulfate activation over 3D urchinlike MoS2/C nanoparticles for accelerating levofloxacin elimination: Optimization and kinetic study
1
2019
... Libin Zeng等〔78〕研究声光联合MoS2/C活化PMS对左氟沙星的降解时发现,用式(26)计算出的协同指数为2.6,表明相对于各单独过程,联合后的活化系统存在出色的协同效果.H. Baharmi等〔79〕通过声光联合活化PDS在20 min内降解了96.3%的三氯乙烯,用式(26)计算出其协同指数为1.62,该系统是通过形成更多自由基实现声光之间的协同效果.J. M. Monteagudo等〔80〕研究紫外、热、Fe2+联合活化PDS时,采用式(27)计算出不同联合活化组合的协同指数为20.09%~89.14%,即均存在协同作用. ...
Degradation of trichloroethylene by sonophotolytic-activated persulfate processes: Optimization using response surface methodology
1
2018
... Libin Zeng等〔78〕研究声光联合MoS2/C活化PMS对左氟沙星的降解时发现,用式(26)计算出的协同指数为2.6,表明相对于各单独过程,联合后的活化系统存在出色的协同效果.H. Baharmi等〔79〕通过声光联合活化PDS在20 min内降解了96.3%的三氯乙烯,用式(26)计算出其协同指数为1.62,该系统是通过形成更多自由基实现声光之间的协同效果.J. M. Monteagudo等〔80〕研究紫外、热、Fe2+联合活化PDS时,采用式(27)计算出不同联合活化组合的协同指数为20.09%~89.14%,即均存在协同作用. ...
In situ chemical oxidation of carbamazepine solutions using persulfate simultaneously activated by heat energy, UV light, Fe2+ ions, and H2O2
1
2015
... Libin Zeng等〔78〕研究声光联合MoS2/C活化PMS对左氟沙星的降解时发现,用式(26)计算出的协同指数为2.6,表明相对于各单独过程,联合后的活化系统存在出色的协同效果.H. Baharmi等〔79〕通过声光联合活化PDS在20 min内降解了96.3%的三氯乙烯,用式(26)计算出其协同指数为1.62,该系统是通过形成更多自由基实现声光之间的协同效果.J. M. Monteagudo等〔80〕研究紫外、热、Fe2+联合活化PDS时,采用式(27)计算出不同联合活化组合的协同指数为20.09%~89.14%,即均存在协同作用. ...
Sonoelectrochemical degradation of propyl paraben: An examination of the synergy in different water matrices
2
2020
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Synergistic degradation of methylparaben on CuFe2O4-rGO composite by persulfate activation
1
2020
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Enhanced persulfate oxidation of organic pollutants and removal of total organic carbons using natural magnetite and microwave irradiation
2
2020
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Magnetic Ni-Co alloy encapsulated N-doped carbon nanotubes for catalytic membrane degradation of emerging contaminants
3
2019
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
... 此外,表 1中还列出了联合活化PS去除污染物研究的水样来源.可以看到,目前对微量有机污染物的联合活化去除研究中还是以实验室模拟水为主.在这些研究中,PS的用量在0.1~2 mol/L,对应的污染物浓度均为μmol/L级别,其中部分实际水中PS的用量更少,表明实验室模拟的污染物浓度普遍高于实际水体中污染物浓度.此外,部分研究会通过在实验室模拟水中添加Cl-等阴离子和部分有机物作为干扰物,以此进一步探讨水基质对污染物去除效果的影响.在研制复合活化PS材料的研究中通常会做这部分工作〔84, 90〕.由于实际废水中存在的基质效应,实验室模拟水得到的结果不能真实反映在实际水处理中的应用效果,联合活化PS去除污染物研究更应该开展以实际废水为实验水介质的污染物去除研究.F. Ghanbari等〔98〕合成了CeO2-Fe3O4纳米复合材料活化PMS,在经过模拟水去除直接红16和苯丙三唑等实验后,将该材料应用在了经过处理的实际纺织废水中,达到了良好的脱色效果(78%脱色率).G. Ozyildiz等〔91〕自制了纳米级还原氧化石墨烯与UV联合活化PDS,可在30 min内完全去除污水处理厂三级废水中的双酚A.尽管在实际废水中联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物的研究已经开展,但是还是需要更多探索. ...
Degradation of ibuprofen by UVA-led/TiO2/persulfate process: Kinetics, mechanism, water matrix effects, intermediates and energy consumption
2
2020
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Synergistic degradation of chloramphenicol by ultrasound-enhanced nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate treatment
3
2020
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
... 由于微量有机物的种类繁多,以及联合活化PS去除污染物的研究还不够充分,不同联合活化方式同污染物之间并没有明显的对应关系.从表 1可以看出,类似的联合活化方式对不同类别的污染物都有良好的去除效果,同类别的污染物可以采用不同的联合活化方式去除.如超声和零价铁联合活化PDS对非甾体抗炎药吡罗昔康〔93〕和抗生素氯霉素〔86〕都能有效去除,而双酚A的去除用Fe/N-C〔89〕联合活化及UV/rGO〔91〕联合活化均有良好效果.这可能是由于所提及到的联合活化方式都是增强了自由基的产生效果,最终体现的是自由基对污染物的氧化. ...
Synergistic multiple active species for the photocatalytic degradation of contaminants by imidazole-modified g-C3N4 coordination with iron phthalocyanine in the presence of peroxymonosulfate
2
2019
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Removal of carbamazepine in water by electro-activated carbon fiber-peroxydisulfate: Comparison, optimization, recycle, and mechanism study
2
2018
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Degradation of organic pollutants by Fe/N Co-doped biochar via peroxymonosulfate activation: Synthesis, performance, mechanism and its potential for practical application
3
2020
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
... 由于微量有机物的种类繁多,以及联合活化PS去除污染物的研究还不够充分,不同联合活化方式同污染物之间并没有明显的对应关系.从表 1可以看出,类似的联合活化方式对不同类别的污染物都有良好的去除效果,同类别的污染物可以采用不同的联合活化方式去除.如超声和零价铁联合活化PDS对非甾体抗炎药吡罗昔康〔93〕和抗生素氯霉素〔86〕都能有效去除,而双酚A的去除用Fe/N-C〔89〕联合活化及UV/rGO〔91〕联合活化均有良好效果.这可能是由于所提及到的联合活化方式都是增强了自由基的产生效果,最终体现的是自由基对污染物的氧化. ...
Quasi-full-visible-light absorption by D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 for synergistic persulfate activation towards efficient photodegradation of micropollutants
2
2019
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
... 此外,表 1中还列出了联合活化PS去除污染物研究的水样来源.可以看到,目前对微量有机污染物的联合活化去除研究中还是以实验室模拟水为主.在这些研究中,PS的用量在0.1~2 mol/L,对应的污染物浓度均为μmol/L级别,其中部分实际水中PS的用量更少,表明实验室模拟的污染物浓度普遍高于实际水体中污染物浓度.此外,部分研究会通过在实验室模拟水中添加Cl-等阴离子和部分有机物作为干扰物,以此进一步探讨水基质对污染物去除效果的影响.在研制复合活化PS材料的研究中通常会做这部分工作〔84, 90〕.由于实际废水中存在的基质效应,实验室模拟水得到的结果不能真实反映在实际水处理中的应用效果,联合活化PS去除污染物研究更应该开展以实际废水为实验水介质的污染物去除研究.F. Ghanbari等〔98〕合成了CeO2-Fe3O4纳米复合材料活化PMS,在经过模拟水去除直接红16和苯丙三唑等实验后,将该材料应用在了经过处理的实际纺织废水中,达到了良好的脱色效果(78%脱色率).G. Ozyildiz等〔91〕自制了纳米级还原氧化石墨烯与UV联合活化PDS,可在30 min内完全去除污水处理厂三级废水中的双酚A.尽管在实际废水中联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物的研究已经开展,但是还是需要更多探索. ...
Effect of nano-scale, reduced graphene oxide on the degradation of bisphenol A in real tertiary treated wastewater with the persulfate/UV-C process
4
2019
... 基于高级氧化的特性,目前应用联合活化PS去除的污染物对象主要是传统生化处理难以除尽的微量有机污染物,集中在药品及个人护理品方面,包括对羟基苯甲酸丙酯等抑菌剂〔81-83〕、布洛芬等非甾体抗炎药〔84-85〕、土霉素等抗生素〔37, 86〕、卡马西平等精神类药物〔87-88〕以及其他类微量有机污染物〔89-91〕.部分代表性污染物及其处理效果如表 1所示. ...
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
... 由于微量有机物的种类繁多,以及联合活化PS去除污染物的研究还不够充分,不同联合活化方式同污染物之间并没有明显的对应关系.从表 1可以看出,类似的联合活化方式对不同类别的污染物都有良好的去除效果,同类别的污染物可以采用不同的联合活化方式去除.如超声和零价铁联合活化PDS对非甾体抗炎药吡罗昔康〔93〕和抗生素氯霉素〔86〕都能有效去除,而双酚A的去除用Fe/N-C〔89〕联合活化及UV/rGO〔91〕联合活化均有良好效果.这可能是由于所提及到的联合活化方式都是增强了自由基的产生效果,最终体现的是自由基对污染物的氧化. ...
... 此外,表 1中还列出了联合活化PS去除污染物研究的水样来源.可以看到,目前对微量有机污染物的联合活化去除研究中还是以实验室模拟水为主.在这些研究中,PS的用量在0.1~2 mol/L,对应的污染物浓度均为μmol/L级别,其中部分实际水中PS的用量更少,表明实验室模拟的污染物浓度普遍高于实际水体中污染物浓度.此外,部分研究会通过在实验室模拟水中添加Cl-等阴离子和部分有机物作为干扰物,以此进一步探讨水基质对污染物去除效果的影响.在研制复合活化PS材料的研究中通常会做这部分工作〔84, 90〕.由于实际废水中存在的基质效应,实验室模拟水得到的结果不能真实反映在实际水处理中的应用效果,联合活化PS去除污染物研究更应该开展以实际废水为实验水介质的污染物去除研究.F. Ghanbari等〔98〕合成了CeO2-Fe3O4纳米复合材料活化PMS,在经过模拟水去除直接红16和苯丙三唑等实验后,将该材料应用在了经过处理的实际纺织废水中,达到了良好的脱色效果(78%脱色率).G. Ozyildiz等〔91〕自制了纳米级还原氧化石墨烯与UV联合活化PDS,可在30 min内完全去除污水处理厂三级废水中的双酚A.尽管在实际废水中联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物的研究已经开展,但是还是需要更多探索. ...
Degradation of propyl paraben by activated persulfate using iron-containing magnetic carbon xerogels: Investigation of water matrix and process synergy effects
1
2018
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Degradation of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug piroxicam by iron activated persulfate: The role of water matrix and ultrasound synergy
2
2018
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
... 由于微量有机物的种类繁多,以及联合活化PS去除污染物的研究还不够充分,不同联合活化方式同污染物之间并没有明显的对应关系.从表 1可以看出,类似的联合活化方式对不同类别的污染物都有良好的去除效果,同类别的污染物可以采用不同的联合活化方式去除.如超声和零价铁联合活化PDS对非甾体抗炎药吡罗昔康〔93〕和抗生素氯霉素〔86〕都能有效去除,而双酚A的去除用Fe/N-C〔89〕联合活化及UV/rGO〔91〕联合活化均有良好效果.这可能是由于所提及到的联合活化方式都是增强了自由基的产生效果,最终体现的是自由基对污染物的氧化. ...
Systematic activation of potassium peroxydisulfate with ZIF-8 via sono-assisted catalytic process: Mechanism and ecotoxicological analysis
1
2020
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Shedding light on the catalytic synergies between Fe(Ⅱ) and PMS in vacuum UV(VUV/Fe/ PMS) photoreactors for accelerated elimination of pharmaceuticals: The case of metformin
1
2020
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Kinetics study of dinitrodiazophenol industrial wastewater treatment by a microwave-coupled ferrous-activated persulfate process
1
2019
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
A new perspective of membrane fouling control by ultraviolet synergic ferrous iron catalytic persulfate〔UV/Fe(Ⅱ)/PS〕 as pretreatment prior to ultrafiltration
1
2020
... 联合活化过硫酸盐应用
| 污染物 | 分类 | 水样来源 | 活化方式 | 实验条件 | 去除效果 | 参考文献 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | 磁性炭干凝胶(CX/Fe) | PDS 500 mg/L,pH=3,超声强度36 W/L | 60 min降解99.6% | 〔92〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸丙酯 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水&二级污水 | US/电化学 | PDS 0.1 mol/L,电流强度3.75 mA/cm2,超声强度36 W/L | 10 min降解89% | 〔81〕 |
| 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 | 防腐剂 | 模拟水 | CuFe2O4-rGO | PDS 5 mmol/L | 120 min降解96% | 〔82〕 |
| 甲硝唑、磺胺嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 松花江水 | 微波辐射/Fe3O4 | PDS 300 mg/L,80 ℃,微波功率300 W | 30 min降解90% | 〔83〕 |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 抑菌剂 | 模拟水 | US/Cu0 | Cu0 64 mg/L,PDS 0.5 mmol/L,超声强度0.4 W/L | 60 min降解96.49% | 〔61〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | Ni-Co@NCNTs | PMS 0.65 mmol/L,25 ℃,活化剂0.05 g/L | 100%去除 | 〔84〕 |
| 布洛芬 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | UVA/TiO2 | PDS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂20 mg/L,光照强度2 mW/cm2 | 20 min降解100% | 〔85〕 |
| 吡罗昔康 | 非甾体抗炎药 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | Fe0 2 mg/L,PDS 20 mg/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔93〕 |
| 四环素、土霉素等 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe0 | Fe0 0.2 mmol/L,PDS 0.2 mmol/L | 60 min降解98.4%磺胺嘧啶 | 〔37〕 |
| 氯霉素 | 抗生素 | 模拟水 | US/Fe0 | PDS 1 mmol/L,Fe0 0.5 g/L,超声强度0.36 W/L | 90 min降解98.1% | 〔86〕 |
| 磺胺甲恶唑 | 抗生素 | 模拟废水&生活污水 | BC/US和BC/solar | PDS 250 mg/L,碳90 mg/L | 30 min降解83% | 〔38〕 |
| 若丹明B | 染料 | 模拟水 | Fe2+/MoS2 | PMS 1 mmol/L,Fe2+ 54 mmol/L | 降解率94.7% | 〔54〕 |
| 酸性蓝7 | 染料 | 模拟水 | US/ZIF-8 | PDS 0.6 mmol/L,ZIF-8 0.6 g/L,pH=8.3,超声功率150 W | 90 min降解82% | 〔94〕 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 | 食品添加剂 | 真实废水 | 热/碱 | pH=12 | 20 min降解93.8% | 〔36〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | Fe/N-C | PMS 0.5 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=6.76,25 ℃ | 60 min降解97% | 〔89〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 模拟水 | D35-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 活化剂50 mg/L,PDS 2 mmol/L | 15 min降解100% | 〔90〕 |
| 双酚A | 化工原材料 | 三级处理废水 | UV/rGO | 活化剂0.01 g/L,PDS 0.125 mmol/L | 30 min降解100% | 〔91〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | g-C3N4-IMA-FePcCl16 | PMS 0.3 mmol/L,活化剂0.1 g/L,pH=7 | 30 min降解95% | 〔87〕 |
| 卡马西平 | 精神类药物 | 模拟水 | 电化学/C | PDS 100 mmol/L,电极电位6 V,pH=3,25 ℃ | 30 min降解98.78% | 〔88〕 |
| 二甲双胍 | 降血糖药 | 模拟水 | UV/Fe | PMS 20 mg/L,Fe 0.05 mg/L,pH=6.3 | 60 min降解100% | 〔95〕 |
| 二硝基重氮酚工业废水 | 炸药 | 工业废水 | 微波辐射/Fe2+ | PDS 8 g/L,微波功率600 W,Fe2+ 0.32 mg/L | 30 min去除71.42% COD | 〔96〕 |
| NOM | | 模拟水 | UV/Fe2+ | PDS 400 μmol/L,Fe2+ 100 μmol/L,pH=7.1,20 ℃ | 将NOM降解为低分子质量物质 | 〔97〕 |
如表 1所示,采用联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物普遍显示出良好的去除效果(去除率 > 90%).众多研究中,联合活化PS去除污染物都表现出远高于单独活化的效果,显示出其巨大的应用潜力.由于过渡金属相对廉价和受到广泛研究的特点,与过渡金属相关的联合活化是最多的,其中Fe是最突出的过渡金属元素.超声、紫外作为输入能量的主要辅助手段,也有很多应用. ...
Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate via nanocomposite CeO2-Fe3O4 for organic pollutants removal: The effect of UV and US irradiation and application for real wastewater
1
2019
... 此外,表 1中还列出了联合活化PS去除污染物研究的水样来源.可以看到,目前对微量有机污染物的联合活化去除研究中还是以实验室模拟水为主.在这些研究中,PS的用量在0.1~2 mol/L,对应的污染物浓度均为μmol/L级别,其中部分实际水中PS的用量更少,表明实验室模拟的污染物浓度普遍高于实际水体中污染物浓度.此外,部分研究会通过在实验室模拟水中添加Cl-等阴离子和部分有机物作为干扰物,以此进一步探讨水基质对污染物去除效果的影响.在研制复合活化PS材料的研究中通常会做这部分工作〔84, 90〕.由于实际废水中存在的基质效应,实验室模拟水得到的结果不能真实反映在实际水处理中的应用效果,联合活化PS去除污染物研究更应该开展以实际废水为实验水介质的污染物去除研究.F. Ghanbari等〔98〕合成了CeO2-Fe3O4纳米复合材料活化PMS,在经过模拟水去除直接红16和苯丙三唑等实验后,将该材料应用在了经过处理的实际纺织废水中,达到了良好的脱色效果(78%脱色率).G. Ozyildiz等〔91〕自制了纳米级还原氧化石墨烯与UV联合活化PDS,可在30 min内完全去除污水处理厂三级废水中的双酚A.尽管在实际废水中联合活化PS去除微量有机污染物的研究已经开展,但是还是需要更多探索. ...
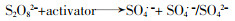
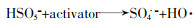

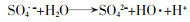
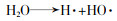
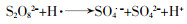
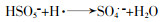
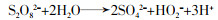
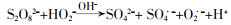
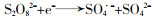

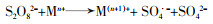
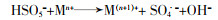
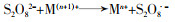

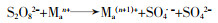
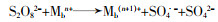
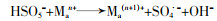
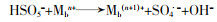

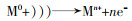
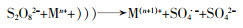

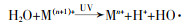
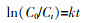
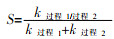

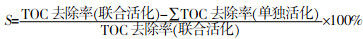
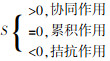



 津公网安备 12010602120337号
津公网安备 12010602120337号