重金属铅为工业废水中常见的污染物之一〔1-2〕。由于重金属无法被微生物降解,且可通过食物链富集,含重金属的废水若不经处理直接排放,会对水体中水生生物的生长繁殖及人类健康构成极大的威胁〔3〕。目前,去除水中重金属铅的方法主要有化学沉淀法、离子交换法、吸附法、物理过滤法等〔4〕。其中,吸附法被认为是从废水中去除重金属的一种最经济有效的方法〔5〕。生物炭是一种黑色的源自生物质热解的多孔材料〔6〕,因其对环境中的重金属显示出很强的亲和力,受到越来越多的关注。然而,尽管生物炭(稻壳生物炭、玉米秸秆生物炭等)对水中重金属有一定的吸附作用,但其吸附能力往往有限〔7-8〕,因此越来越多的学者致力于生物炭的改性,以提高生物炭的吸附能力〔9〕。
为促进棉花废弃物的资源化利用,本研究以棉籽壳制备的生物炭为原始炭(BC),对其进行KMnO4改性,制得改性生物炭(BC-Mn),并通过实验研究了BC-Mn对水中铅的吸附性能。该项研究可为水体重金属污染稳定化修复技术的开发提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 生物炭的制备
制备生物炭(BC)的原料棉籽壳购于山东德州。将棉籽壳用蒸馏水清洗干净,烘干,粉碎,过筛(0.15 mm)。称取200 g棉籽壳粉末于管式炉中,在恒温缺氧的条件下,制备250、350、450、550 ℃ 4种不同温度条件的生物炭,升温速率均为10 ℃/min,热解时间均为2 h。
分别取0.1 g上述4种条件下制备的生物炭置于装有50 mL 300 mg/L Pb2+溶液的三角瓶中,在摇床中以140 r/min振荡反应24 h。震荡结束后,过0.45 μm滤膜,用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,安捷伦7700 icp-ms)测定滤液中铅的浓度,计算各生物炭对铅的吸附量。结果表明,450 ℃条件下制备的生物炭对铅的吸附量最大,为64.45 mg/g。因此,选取450 ℃条件下制备的生物炭进行改性生物炭的制备。
1.2 改性生物炭的制备
按照生物炭与KMnO4的质量比为2∶1制备改性生物炭。将上述配比的材料和500 mL超纯水置于500 mL三角瓶中,超声分散2 h。然后用抽滤装置以超纯水进行洗涤过滤,将溶液洗至无色。收集改性生物炭,于65 ℃烘干至恒重,标记为BC-Mn。
1.3 实验方法
取一定量的吸附剂置于装有50 mL一定浓度Pb2+溶液的三角瓶中,在摇床中以140 r/min振荡反应一定时间。震荡结束后,过0.45 μm滤膜,用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,安捷伦7700 icp-ms)测定滤液中铅的浓度。如无特别说明,实验条件为初始Pb2+质量浓度300 mg/L,不调节pH,吸附剂投加量2 g/L,反应温度30 ℃,反应时间24 h。用0.1 mol/LHNO3和NaOH溶液调节pH。吸附实验所用Pb2+水溶液均由硝酸铅(AR)配制而成。
2 实验结果
2.1 制备样品的表征
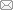
图 1为改性前后生物炭样品的SEM表征结果。
图1
为了进一步探讨BC-Mn的性能,采用BET法计算生物炭的比表面积,如表 1所示。
表1 生物炭的比表面积和孔径结构
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 外表面积/(m2·g-1) | 孔体积/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm |
| BC | 9.76 | 14.865 | 0.015 | 6.214 |
| BC-Mn | 261.62 | 28.159 | 0.131 | 2.001 7 |
2.2 吸附实验结果
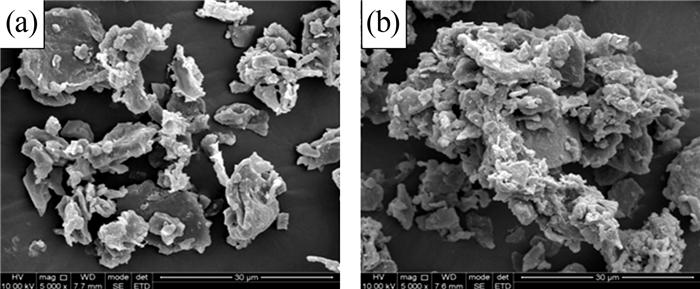
2.2.1 pH对吸附效果的影响
图2
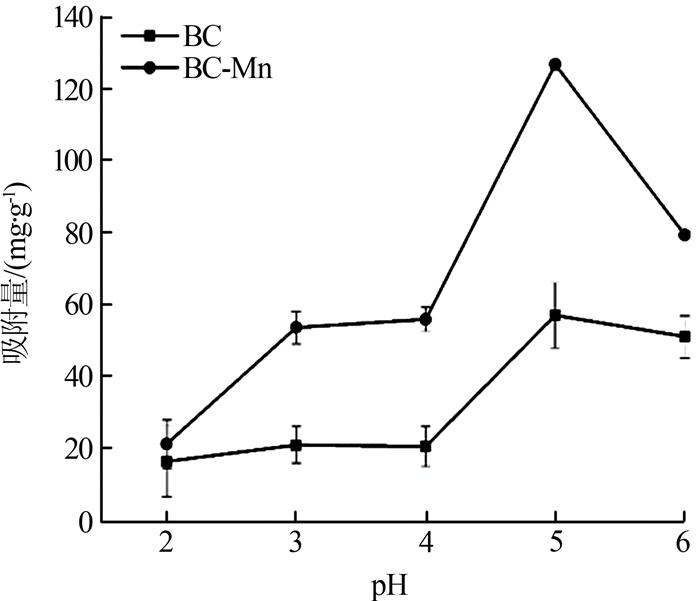
2.2.2 吸附剂投加量对吸附效果的影响
吸附剂投加量对吸附效果的影响如图 3所示。
图3
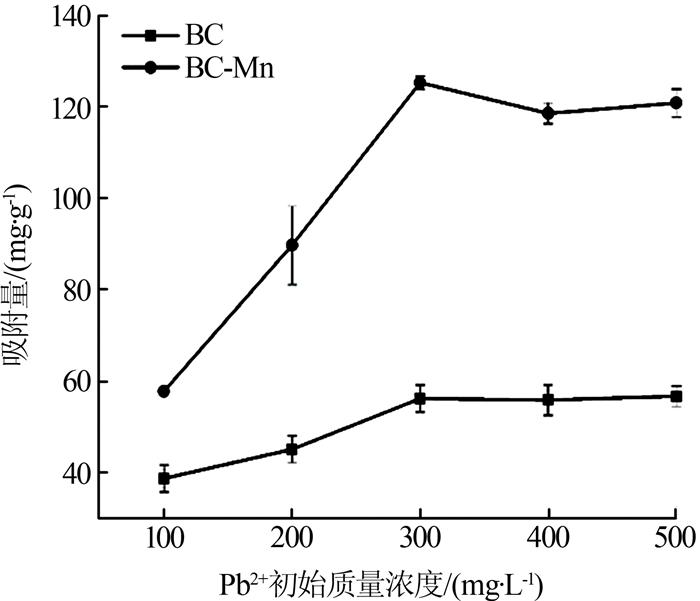
2.2.3 初始Pb2+浓度对吸附效果的影响
初始Pb2+浓度对吸附效果的影响如图 4所示。
图4
由图 4可知,当初始Pb2+质量浓度为300 mg/L时,BC-Mn对Pb2+的吸附量达到最大,为125.33 mg/g。随着初始Pb2+浓度的进一步增大,BC-Mn对Pb2+的吸附量下降,这主要是因为BC-Mn上可吸附Pb2+的活性位点已经达到饱和。
2.2.4 吸附动力学结果
在溶液pH为5,反应时间分别为5、15、30、60、120、240、360、480、600、720、840、960、1 200、1 440 min的条件下进行吸附动力学实验,并采用拟一级动力学模型、拟二级动力学模型和粒子内扩散模型对实验数据进行拟合,结果如表 2所示。
表2 BC-Mn吸附动力学模型拟合参数
| 重金属 | 拟一级动力学模型 | 拟二级动力学模型 | 粒子内扩散模型 | |||||||
| K1/ min-1 | qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | K2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | K3/(mg·g-1·min-0.5) | R2 | |||
| Pb | 0.003 | 82.872 | 0.937 | 0.000 1 | 138.504 | 0.996 | 2.438 | 0.878 | ||
2.2.5 等温吸附结果
在溶液pH为5,初始Pb2+质量浓度分别为10、25、50、100、200、300、400、500 mg/L,温度分别为293、303、313 K的条件下进行等温吸附实验,并利用Langmuir、Freundlich等温吸附模型对实验数据进行拟合,结果如表 3所示。
表3 Freundlich与Langmuir模型拟合参数
| 温度/K | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | ||
| 293 | 4.308 | 113.924 | 0.849 | 47.286 | 0.182 | 0.810 | |
| 303 | 6.013 | 128.089 | 0.998 | 62.311 | 0.133 | 0.769 | |
| 313 | 5.453 | 131.756 | 0.967 | 60.350 | 0.159 | 0.769 | |
表 4是BC-Mn吸附Pb2+的热力学参数。
表4 热力学参数
| 温度/K | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔS/(J·mol-1·K-1) |
| 293 | -3.556 | ||
| 303 | -4.509 | 14.26 | 0.06 |
| 313 | -4.78 |
由表 4可知,ΔG为负值,且随温度的升高,ΔG减小,表明该吸附过程可以自发进行。ΔH为正值,表明该吸附是一个吸热过程且偏向于化学吸附,升高温度有利于吸附的进行。
2.2.6 模拟废水实验结果
表5 不同BC-Mn投加量下处理后废水离子浓度
| BC-Mn/(g·L-1) | pH | 重金属离子质量浓度/(mg·L-1) | ||||
| Pb | Cd | Zn | Cu | Ni | ||
| 0 | 5.5 | 2.934 | 4.62 | 16.41 | 8.77 | 1.43 |
| 1 | 5.5 | 0.099 8 | 2.54 | 8.143 | 0.51 | 0.835 |
| 2 | 5.5 | 0.038 | 0.29 | 3.189 | 0.12 | 0.191 |
| 3 | 5.5 | 0.029 | 0.064 | 1.618 | 0.056 | 0.147 |
| 4 | 5.5 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.698 | 0.033 | 0.073 |
| 国标 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.05 | ≤1.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | |
实验结果表明,BC-Mn投加量为1 g/L时,处理后废水中的Pb2+浓度已达到《铅、锌工业污染物排放标准》(GB 25466—2010)的要求。随着BC-Mn投加量的不断增加,在4 g/L的投加量下,其他几种共存重金属的去除效果也都达到了工业污染物排放标准。
3 结论
(1)相较于未改性生物炭,经高锰酸钾改性后的BC-Mn的比表面积显著增大,吸附能力显著提高。
(2)BC-Mn吸附Pb2+的最佳条件:生物炭投加量为2 g/L,pH为5,初始Pb2+质量浓度为300 mg/L。
(3)BC-Mn对Pb2+的吸附过程符合拟二级动力学模型及Langmuir等温吸附模型,该吸附过程是自发进行的吸热过程。
(4)工业废水模拟实验表明,BC-Mn是一种吸附性能良好且具有实际应用能力的重金属吸附剂。
参考文献
New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.07.019 [本文引用: 1]
Assessing the concentration and potential dietary risk of heavy metals in vegetables at a Pb/Zn mine site, China
[J].DOI:10.1007/s12665-011-0992-1 [本文引用: 1]
H2O2 treatment enhanced the heavy metals removal by manure biochar in aqueous solutions
[J].
Application of crop straw derived biochars to Cu(Ⅱ) contaminated Ultisol: Evaluating role of alkali and organic functional groups in Cu(Ⅱ) immobilization
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.161 [本文引用: 1]
Batch and column sorption of arsenic onto iron-impregnated biochar synthesized through hydrolysis
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.009 [本文引用: 1]
Biochar reduces the bioavailability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals
[J].
Investigating the sorption behavior of cadmium from aqueous solution by potassium permanganate-modified biochar: Quantify mechanism and evaluate the modification method
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11356-017-1145-1 [本文引用: 1]
Adsorption behavior of nickel(Ⅱ) onto cashew nut shell: Equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanism and process design
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.010 [本文引用: 2]
Unraveling sorption of nickel from aqueous solution by KMnO4 and KOH-modified peanut shell biochar: Implicit mechanism
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.007 [本文引用: 1]
Corrigendum: Competitive sorption of Pb(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ) and Ni(Ⅱ) on carbonaceous nanofibers: A spectroscopic and modeling approach
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.002 [本文引用: 1]
Investigating the adsorption behavior and the relative distribution of Cd2+ sorption mechanisms on biochars by different feedstock
[J].
Enhanced adsorption for Pb(Ⅱ) and Cd(Ⅱ) of magnetic rice husk biochar by KMnO4 modification
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11356-019-04321-z [本文引用: 1]
Multi-component adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ), Cd(Ⅱ) and Ni(Ⅱ) onto microwave-functionalized cellulose: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanisms and application for electroplating wastewater purification
[J].



 津公网安备 12010602120337号
津公网安备 12010602120337号