The global rise of zero liquid discharge for wastewater management: Drivers, technologies, and future directions
1
2016
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment
1
2011
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
膜处理技术在废酸回收中的应用
1
2016
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
温度极化对带有膜热交换器的溴化锂吸收式制冷系统性能的影响分析
1
2016
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
Development of robust and superhydrophobic membranes to mitigate membrane scaling and fouling in membrane distillation
1
2020
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
Experimental and theoretical analyses of temperature polarization effect in vacuum membrane distillation
2
2014
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
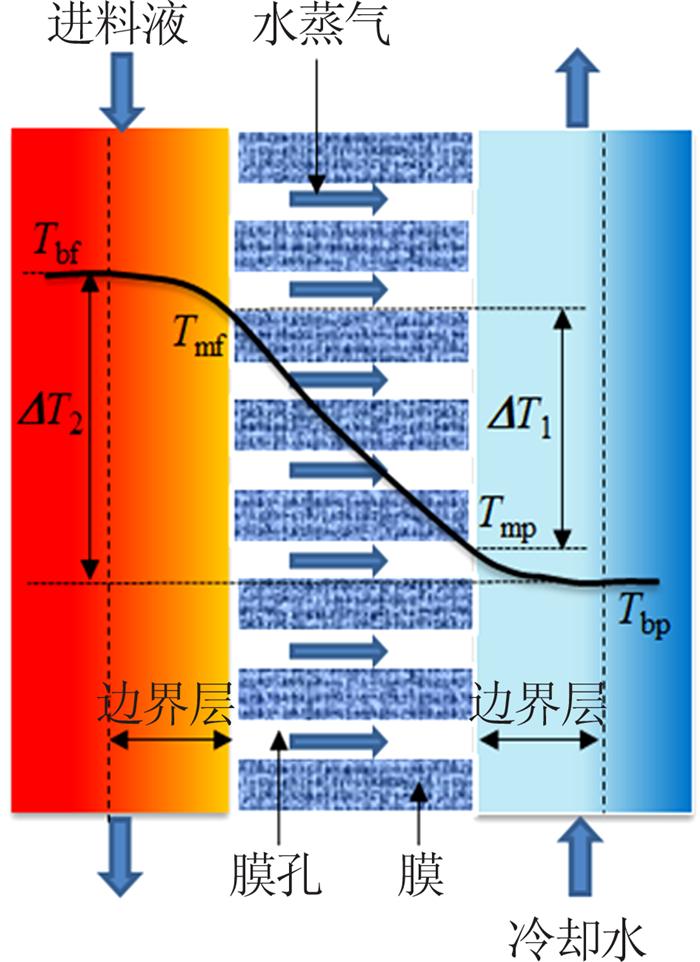
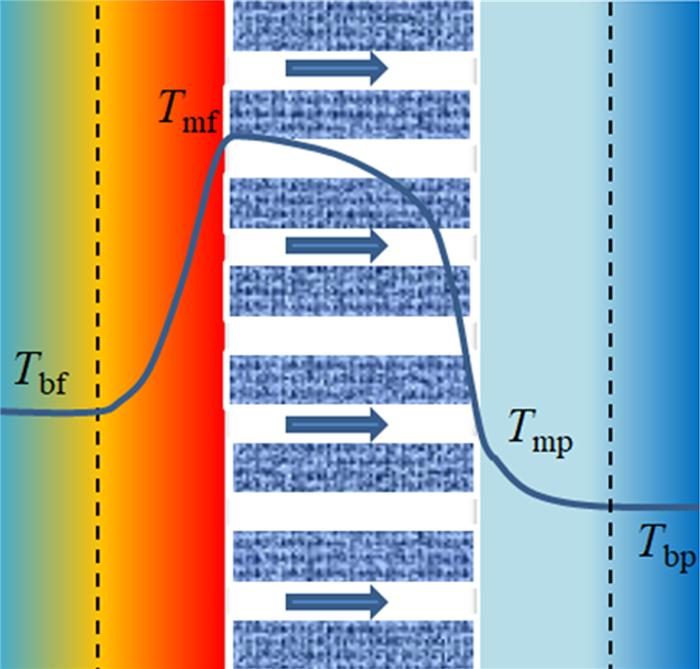
... MD是一种非等温的物理分离技术.进料液的蒸发促使进料侧膜孔处形成汽-液界面,水蒸汽扩散穿过疏水膜在渗透侧冷凝〔10〕.如图 1所示,在该过程中,进料侧膜表面温度(Tmf)低于进料液温度(Tbf),渗透侧膜表面温度(Tmp)高于冷却水温度(Tbp),由此导致了温度极化现象.膜两侧温度变化处与膜表面之间形成温度边界层,该层越厚,膜与料液间的温差则越大,温度极化越明显〔11〕.在直接接触膜蒸馏(DCMD)、气隙膜蒸馏(AGMD)和气扫膜蒸馏(SGMD)中,温度极化由膜两侧的温差所导致〔12〕,而真空膜蒸馏(VMD)的渗透侧由于存在负压,渗透侧的热量损失可忽略不计,故温度极化只产生于进料侧〔6〕. ...
Photothermal nanocomposite membranes for direct solar membrane distillation
2
2017
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
... 近年来,利用膜表面加热冷进料的研究逐渐增多.比如,在PVDF膜上添加SiO2/Au纳米涂层,利用其优良的光热和局部加热性能将太阳能转化为膜表面的热能,可使渗透通量提高33.0%〔7〕.将纳米炭黑颗粒分散到聚乙烯醇(PVA)溶液中,再电纺到PVDF膜上,形成由负载炭黑的PVA纳米纤维与PVDF疏水膜组成的双层结构,当紫外线或太阳辐射照射到膜表面时就会产生局部加热的效果,进而将热量传递给冷料液.在聚焦太阳光下,使用小规模的膜组件可获得5.4 L/(m2·h)的渗透通量,盐分截留率大于99.5%〔41〕. ...
Performance improvements by embedded spacer in direct contact membrane distillation-computational study
1
2019
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
Electrothermally driven membrane distillation for low-energy consumption and wetting mitigation
2
2019
... 高盐废水的脱盐技术可促进工业废水(如油气开采废水)或海水淡化浓盐水的有效处理与处置〔1〕.由于高盐水的渗透压非常高,因此无法使用压力驱动膜分离技术如反渗透(RO)来淡化.热脱盐工艺被认为是目前高盐水脱盐的唯一有效手段〔2〕.膜蒸馏(MD)是一种新兴的热脱盐工艺,它以多孔疏水膜两侧之间存在的蒸汽压差为驱动力,蒸汽分子透过膜孔后冷凝富集,实现水与污染物的高效分离.与传统的热脱盐工艺(如多效蒸馏和多级闪蒸)相比,MD所需的传热设备简单并且可以利用低品质热源,同时占地面积较小,具有模块化特点和可扩展性〔3-4〕;与压力驱动型工艺(如RO)相比,MD膜具有较大的膜孔径,因此更耐膜污染,特别适合因盐度太高(大于80 g/L)而无法采用RO的场合使用〔5〕.然而,MD过程中普遍存在温度极化现象,其可导致传质驱动力降低40%~65%,进而使渗透通量降低且能耗增加〔6-7〕.因此,温度极化成为制约MD性能的瓶颈因素之一.为减轻温度极化现象,研究人员做了大量研究,比如,通过优化组件设计来改变料液流态〔8〕,研制复合膜实现对冷进料的加热等〔9〕.笔者主要针对温度极化对MD过程中传热和传质的影响以及减轻温度极化的方法作以综述,以期深入理解MD过程中驱动力的形成以及渗透通量提高的规律. ...
... Kuiling Li等〔9〕利用还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)优良的热导电性能,在PTFE膜表面喷涂RGO,制备出可以实现反焦耳加热的复合膜.在AGMD研究中将复合膜置于气隙侧且不与进料液接触,故可避免因反焦耳加热时水的电解和膜的降解.实验中90.56%的热量可传递给冷料液,温度极化现象得到缓解,同时也减轻了膜孔的润湿现象.A. Anvari等〔44〕将PTFE膜上喷涂氧化铁-碳纳米管,制备出可在高频磁场中感应加热的复合膜.在VMD中应用该复合膜之后,渗透通量提高了5.3倍,能耗降低了83%. ...
Titanium nitride nanoparticle embedded membrane for photothermal membrane distillation
1
2020
... MD是一种非等温的物理分离技术.进料液的蒸发促使进料侧膜孔处形成汽-液界面,水蒸汽扩散穿过疏水膜在渗透侧冷凝〔10〕.如图 1所示,在该过程中,进料侧膜表面温度(Tmf)低于进料液温度(Tbf),渗透侧膜表面温度(Tmp)高于冷却水温度(Tbp),由此导致了温度极化现象.膜两侧温度变化处与膜表面之间形成温度边界层,该层越厚,膜与料液间的温差则越大,温度极化越明显〔11〕.在直接接触膜蒸馏(DCMD)、气隙膜蒸馏(AGMD)和气扫膜蒸馏(SGMD)中,温度极化由膜两侧的温差所导致〔12〕,而真空膜蒸馏(VMD)的渗透侧由于存在负压,渗透侧的热量损失可忽略不计,故温度极化只产生于进料侧〔6〕. ...
太阳能中空纤维空气隙膜蒸馏海水淡化性能研究
1
2016
... MD是一种非等温的物理分离技术.进料液的蒸发促使进料侧膜孔处形成汽-液界面,水蒸汽扩散穿过疏水膜在渗透侧冷凝〔10〕.如图 1所示,在该过程中,进料侧膜表面温度(Tmf)低于进料液温度(Tbf),渗透侧膜表面温度(Tmp)高于冷却水温度(Tbp),由此导致了温度极化现象.膜两侧温度变化处与膜表面之间形成温度边界层,该层越厚,膜与料液间的温差则越大,温度极化越明显〔11〕.在直接接触膜蒸馏(DCMD)、气隙膜蒸馏(AGMD)和气扫膜蒸馏(SGMD)中,温度极化由膜两侧的温差所导致〔12〕,而真空膜蒸馏(VMD)的渗透侧由于存在负压,渗透侧的热量损失可忽略不计,故温度极化只产生于进料侧〔6〕. ...
膜蒸馏技术在工业低温余热废水处理上的应用
1
2019
... MD是一种非等温的物理分离技术.进料液的蒸发促使进料侧膜孔处形成汽-液界面,水蒸汽扩散穿过疏水膜在渗透侧冷凝〔10〕.如图 1所示,在该过程中,进料侧膜表面温度(Tmf)低于进料液温度(Tbf),渗透侧膜表面温度(Tmp)高于冷却水温度(Tbp),由此导致了温度极化现象.膜两侧温度变化处与膜表面之间形成温度边界层,该层越厚,膜与料液间的温差则越大,温度极化越明显〔11〕.在直接接触膜蒸馏(DCMD)、气隙膜蒸馏(AGMD)和气扫膜蒸馏(SGMD)中,温度极化由膜两侧的温差所导致〔12〕,而真空膜蒸馏(VMD)的渗透侧由于存在负压,渗透侧的热量损失可忽略不计,故温度极化只产生于进料侧〔6〕. ...
温度极化对膜蒸馏过程的影响研究
1
2004
... 温度极化系数(TPC)是衡量温度极化程度的重要指标.令Tmf-Tmp =ΔT1,Tbf-Tbp=ΔT2,则DCMD、AGMD和SGMD的TPC可用式(1)表示〔13〕,VMD的TPC可用式(2)表示〔14〕. ...
A comprehensive review of vacuum membrane distillation technique
1
2015
... 温度极化系数(TPC)是衡量温度极化程度的重要指标.令Tmf-Tmp =ΔT1,Tbf-Tbp=ΔT2,则DCMD、AGMD和SGMD的TPC可用式(1)表示〔13〕,VMD的TPC可用式(2)表示〔14〕. ...
Computational fluid dynamic(CFD) opportunities applied to the membrane distillation process: State-of-the-art and perspectives
1
2016
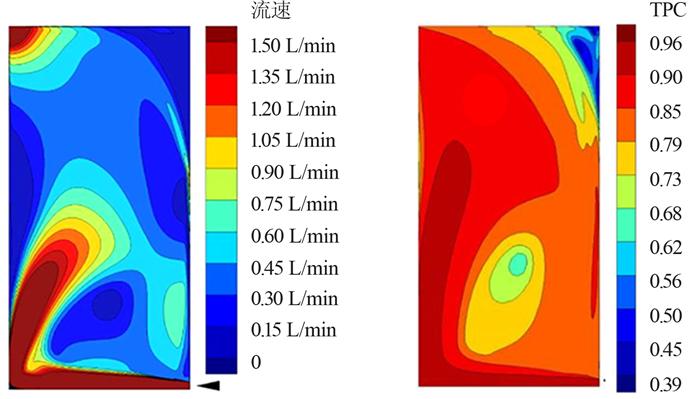
... 进料液流速对温度极化有显著影响.在较低的进料流速下边界层较厚,传热阻力大,阻碍了由料液层向膜表面的传热,加剧了温度极化现象.由于TPC的计算需要获得膜表面温度的数据,但其准确测量存在一定难度,因此,目前较多是通过建立计算流体动力学(CFD)模型来研究温度极化〔15〕.比如,S. Soukane等〔16〕利用CFD模拟了反应器中进料流速分布和进料侧膜表面的TPC分布,得到流速分布与TPC的关系,如图 2所示,TPC最大值出现在对应的流速最大处,而最小值对应于流速最低处.这是因为流速的增加使进料液对温度边界层的扰动增强,减小了边界层的厚度,ΔT1增加,使TPC增加.当流速从0.4 L/min提高到2.0 L/min时,TPC可提高81%〔17〕.此外,湍流条件下料液对边界层的扰动更明显.在DCMD中,层流状态下的TPC一般小于0.6,而在湍流状态下将大于0.85〔18〕.在SGMD中,湍流状态下的TPC可比层流状态下提高76%〔19〕. ...
Effect of feed flow pattern on the distribution of permeate fluxes in desalination by direct contact membrane distillation
1
2017
... 进料液流速对温度极化有显著影响.在较低的进料流速下边界层较厚,传热阻力大,阻碍了由料液层向膜表面的传热,加剧了温度极化现象.由于TPC的计算需要获得膜表面温度的数据,但其准确测量存在一定难度,因此,目前较多是通过建立计算流体动力学(CFD)模型来研究温度极化〔15〕.比如,S. Soukane等〔16〕利用CFD模拟了反应器中进料流速分布和进料侧膜表面的TPC分布,得到流速分布与TPC的关系,如图 2所示,TPC最大值出现在对应的流速最大处,而最小值对应于流速最低处.这是因为流速的增加使进料液对温度边界层的扰动增强,减小了边界层的厚度,ΔT1增加,使TPC增加.当流速从0.4 L/min提高到2.0 L/min时,TPC可提高81%〔17〕.此外,湍流条件下料液对边界层的扰动更明显.在DCMD中,层流状态下的TPC一般小于0.6,而在湍流状态下将大于0.85〔18〕.在SGMD中,湍流状态下的TPC可比层流状态下提高76%〔19〕. ...
Influence of high range of mass transfer coefficient and convection heat transfer on direct contact membrane distillation performance
2
2018
... 进料液流速对温度极化有显著影响.在较低的进料流速下边界层较厚,传热阻力大,阻碍了由料液层向膜表面的传热,加剧了温度极化现象.由于TPC的计算需要获得膜表面温度的数据,但其准确测量存在一定难度,因此,目前较多是通过建立计算流体动力学(CFD)模型来研究温度极化〔15〕.比如,S. Soukane等〔16〕利用CFD模拟了反应器中进料流速分布和进料侧膜表面的TPC分布,得到流速分布与TPC的关系,如图 2所示,TPC最大值出现在对应的流速最大处,而最小值对应于流速最低处.这是因为流速的增加使进料液对温度边界层的扰动增强,减小了边界层的厚度,ΔT1增加,使TPC增加.当流速从0.4 L/min提高到2.0 L/min时,TPC可提高81%〔17〕.此外,湍流条件下料液对边界层的扰动更明显.在DCMD中,层流状态下的TPC一般小于0.6,而在湍流状态下将大于0.85〔18〕.在SGMD中,湍流状态下的TPC可比层流状态下提高76%〔19〕. ...
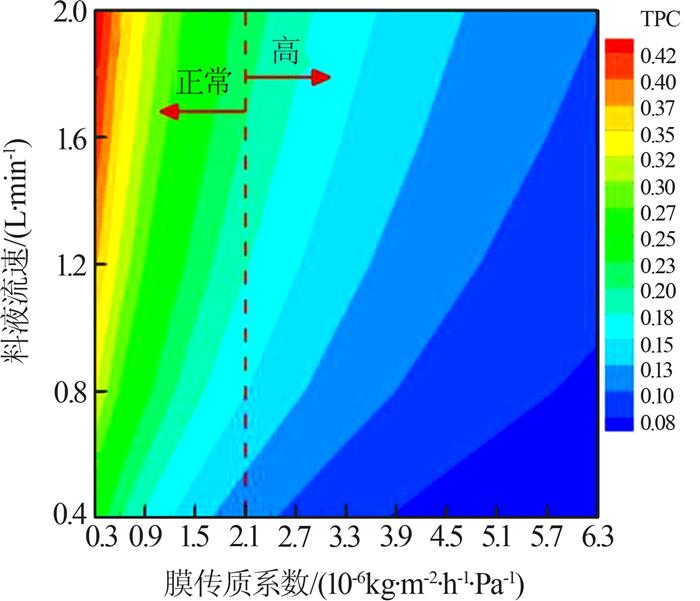
... 此外,TPC的数值会随着疏水膜传质系数的增大而减小,从而加剧温度极化现象.在正常传质系数〔 < 2.1×10-6 kg/(m2·h·Pa)〕下,TPC的变化更易受料液流速的影响;当传质系数较高时,传热阻力会集中在边界层上,此时需要更大的流速变化来扰动边界层,其对TPC的影响减弱(图 3)〔17〕. ...
膜蒸馏过程传递机理研究进展(Ⅰ)直接接触式膜蒸馏
2
2008
... 进料液流速对温度极化有显著影响.在较低的进料流速下边界层较厚,传热阻力大,阻碍了由料液层向膜表面的传热,加剧了温度极化现象.由于TPC的计算需要获得膜表面温度的数据,但其准确测量存在一定难度,因此,目前较多是通过建立计算流体动力学(CFD)模型来研究温度极化〔15〕.比如,S. Soukane等〔16〕利用CFD模拟了反应器中进料流速分布和进料侧膜表面的TPC分布,得到流速分布与TPC的关系,如图 2所示,TPC最大值出现在对应的流速最大处,而最小值对应于流速最低处.这是因为流速的增加使进料液对温度边界层的扰动增强,减小了边界层的厚度,ΔT1增加,使TPC增加.当流速从0.4 L/min提高到2.0 L/min时,TPC可提高81%〔17〕.此外,湍流条件下料液对边界层的扰动更明显.在DCMD中,层流状态下的TPC一般小于0.6,而在湍流状态下将大于0.85〔18〕.在SGMD中,湍流状态下的TPC可比层流状态下提高76%〔19〕. ...
... 基于Knudsen扩散和分子扩散的联合效应,膜的渗透性依赖于膜厚度、孔隙率、孔径和曲折因子〔19〕.在层流和湍流两种流态中,TPC随膜厚度的减小而减小,随孔隙率的增大而减小,随曲折因子的减小而减小.这是因为,当膜厚度小、孔隙率大且曲折因子小时,蒸汽的渗透速率增大,导致进料侧膜表面温度降低程度增大,即ΔT1减小,故TPC减小〔18〕. ...
Computational study of sweeping gas membrane distillation process-Flux performance and polarization characteristics
2
2020
... 进料液流速对温度极化有显著影响.在较低的进料流速下边界层较厚,传热阻力大,阻碍了由料液层向膜表面的传热,加剧了温度极化现象.由于TPC的计算需要获得膜表面温度的数据,但其准确测量存在一定难度,因此,目前较多是通过建立计算流体动力学(CFD)模型来研究温度极化〔15〕.比如,S. Soukane等〔16〕利用CFD模拟了反应器中进料流速分布和进料侧膜表面的TPC分布,得到流速分布与TPC的关系,如图 2所示,TPC最大值出现在对应的流速最大处,而最小值对应于流速最低处.这是因为流速的增加使进料液对温度边界层的扰动增强,减小了边界层的厚度,ΔT1增加,使TPC增加.当流速从0.4 L/min提高到2.0 L/min时,TPC可提高81%〔17〕.此外,湍流条件下料液对边界层的扰动更明显.在DCMD中,层流状态下的TPC一般小于0.6,而在湍流状态下将大于0.85〔18〕.在SGMD中,湍流状态下的TPC可比层流状态下提高76%〔19〕. ...
... 基于Knudsen扩散和分子扩散的联合效应,膜的渗透性依赖于膜厚度、孔隙率、孔径和曲折因子〔19〕.在层流和湍流两种流态中,TPC随膜厚度的减小而减小,随孔隙率的增大而减小,随曲折因子的减小而减小.这是因为,当膜厚度小、孔隙率大且曲折因子小时,蒸汽的渗透速率增大,导致进料侧膜表面温度降低程度增大,即ΔT1减小,故TPC减小〔18〕. ...
Impact of module design on heat transfer in membrane distillation
2
2020
... 在MD中,传热过程可以分为进料侧传热、跨膜传热和渗透侧传热三个阶段〔20〕. ...
... 渗透侧传热的方式为对流传热,即热量从膜表面通过热边界层传递到渗透侧,热通量由式(5)表示〔20〕. ...
气扫式膜蒸馏传质传热过程
1
2009
... 进料侧传热的方式为对流传热,即热量通过热边界层传递到进料侧膜表面.这部分热通量计算通常如式(3)所示〔21〕,且适用于所有MD类型. ...
A review on membrane applications and transport mechanisms in vacuum membrane distillation
2
2017
... 其中,hf大小受料液边界层的影响,边界层越厚则hf越小.温度极化现象的存在使得热通量随Tbf与Tmf差值的增大而增大,但边界层增加了额外的传热阻力,热损失增大,使传热过程中热通量减少〔22〕.温度极化越明显则热损失越大.研究表明MD过程中热量损失的80%是由温度极化导致的,此外还使传热效率降低〔23-24〕. ...
... 由式(6)可知,渗透通量的大小与跨膜蒸汽压差成正比,膜两侧的蒸汽压差是跨膜传质的主要驱动力,其值则随ΔT1的减小而降低〔28〕.当温度极化现象严重时则表现为ΔT1减小,将导致传质驱动力降低,渗透通量降低〔22〕. ...
膜蒸馏过程传递机理研究进展(Ⅱ)气隙式膜蒸馏
1
2009
... 其中,hf大小受料液边界层的影响,边界层越厚则hf越小.温度极化现象的存在使得热通量随Tbf与Tmf差值的增大而增大,但边界层增加了额外的传热阻力,热损失增大,使传热过程中热通量减少〔22〕.温度极化越明显则热损失越大.研究表明MD过程中热量损失的80%是由温度极化导致的,此外还使传热效率降低〔23-24〕. ...
Experimental and theoretical evaluation of temperature polarization phenomenon in direct contact membrane distillation
2
2013
... 其中,hf大小受料液边界层的影响,边界层越厚则hf越小.温度极化现象的存在使得热通量随Tbf与Tmf差值的增大而增大,但边界层增加了额外的传热阻力,热损失增大,使传热过程中热通量减少〔22〕.温度极化越明显则热损失越大.研究表明MD过程中热量损失的80%是由温度极化导致的,此外还使传热效率降低〔23-24〕. ...
... 此外,渗透通量也可通过TPC的变化反映出来.当TPC从0.65增加到0.84时渗透通量可提高25%,TPC从0.84增加到0.9时,渗透通量可提高33%,且TPC越大时,渗透通量的变化越明显〔24〕. ...
太阳能膜蒸馏实验与数学建模
1
2010
... 跨膜传热由热量在膜上的传导传热(显热)以及水蒸气通过膜孔时的传热(潜热)两部分组成.跨膜传热一般可用式(4)表示〔25〕. ...
膜蒸馏过程传递机理研究进展(Ⅲ)真空膜蒸馏
1
2009
... 温度极化对渗透侧传热的影响与进料侧相似,边界层的热阻力使热通量降低.但式(5)不适用于AGMD和VMD.这是因为AGMD的冷凝侧存在气隙,传热机理复杂,目前的研究对AGMD渗透侧传热并没有统一的公式.而在VMD中,由于存在负压,渗透侧热边界层引起的热损失可以忽略不计〔26〕. ...
Membrane distillation at the water-energy nexus: Limits, opportunities, and challenges
1
2018
... MD中的传质表现为蒸汽透过膜后所收集的渗透液,可用渗透通量表示〔27〕: ...
The effect of spacer orientations on temperature polarization in a direct contact membrane distillation process using 3-d CFD modeling
1
2019
... 由式(6)可知,渗透通量的大小与跨膜蒸汽压差成正比,膜两侧的蒸汽压差是跨膜传质的主要驱动力,其值则随ΔT1的减小而降低〔28〕.当温度极化现象严重时则表现为ΔT1减小,将导致传质驱动力降低,渗透通量降低〔22〕. ...
Hollow fiber membranes with different external corrugated surfaces for desalination by membrane distillation
1
2017
... 由于料液的流态影响到温度极化的程度,因此通过对MD组件的优化以改善料液流态可减轻温度极化.L. García-Fernández等〔29〕采用湿法纺丝技术制备出具有波纹状外表面的聚偏氟乙烯中空纤维膜,波纹状外表面起到微湍流促进剂的作用,使进料液对边界层的扰动增加,减轻了温度极化,从而使渗透通量提高了36%,盐截留率保持在99.9%.M. M. A. Shirazi等〔30〕对热侧和冷侧的流道深度分别为2、4、6 mm的膜组件进行研究,结果表明减小热侧膜组件深度和增加冷侧膜组件深度有助于减轻温度极化.这是因为,热侧流道深度的减小会使料液流速增大,膜界面湍流水平增加,温度边界层减小.I. Janajreh等〔31〕在DCMD的研究中,设计流道坡度分别为0.012、0.024和0.036的反应器,发现坡度的增大可使料液流速逐渐增大,进而可促使ΔT1增大,与零坡度流道相比,TPC分别提高了6.0%、13.8%和23%.当坡度为0.036时,传热效率从15%提升到48%,渗透通量增加2.6倍. ...
Evaluation of commercial PTFE membranes in desalination by direct contact membrane distillation
1
2014
... 由于料液的流态影响到温度极化的程度,因此通过对MD组件的优化以改善料液流态可减轻温度极化.L. García-Fernández等〔29〕采用湿法纺丝技术制备出具有波纹状外表面的聚偏氟乙烯中空纤维膜,波纹状外表面起到微湍流促进剂的作用,使进料液对边界层的扰动增加,减轻了温度极化,从而使渗透通量提高了36%,盐截留率保持在99.9%.M. M. A. Shirazi等〔30〕对热侧和冷侧的流道深度分别为2、4、6 mm的膜组件进行研究,结果表明减小热侧膜组件深度和增加冷侧膜组件深度有助于减轻温度极化.这是因为,热侧流道深度的减小会使料液流速增大,膜界面湍流水平增加,温度边界层减小.I. Janajreh等〔31〕在DCMD的研究中,设计流道坡度分别为0.012、0.024和0.036的反应器,发现坡度的增大可使料液流速逐渐增大,进而可促使ΔT1增大,与零坡度流道相比,TPC分别提高了6.0%、13.8%和23%.当坡度为0.036时,传热效率从15%提升到48%,渗透通量增加2.6倍. ...
Assessment of direct contact membrane distillation under different configurations, velocities and membrane properties
1
2017
... 由于料液的流态影响到温度极化的程度,因此通过对MD组件的优化以改善料液流态可减轻温度极化.L. García-Fernández等〔29〕采用湿法纺丝技术制备出具有波纹状外表面的聚偏氟乙烯中空纤维膜,波纹状外表面起到微湍流促进剂的作用,使进料液对边界层的扰动增加,减轻了温度极化,从而使渗透通量提高了36%,盐截留率保持在99.9%.M. M. A. Shirazi等〔30〕对热侧和冷侧的流道深度分别为2、4、6 mm的膜组件进行研究,结果表明减小热侧膜组件深度和增加冷侧膜组件深度有助于减轻温度极化.这是因为,热侧流道深度的减小会使料液流速增大,膜界面湍流水平增加,温度边界层减小.I. Janajreh等〔31〕在DCMD的研究中,设计流道坡度分别为0.012、0.024和0.036的反应器,发现坡度的增大可使料液流速逐渐增大,进而可促使ΔT1增大,与零坡度流道相比,TPC分别提高了6.0%、13.8%和23%.当坡度为0.036时,传热效率从15%提升到48%,渗透通量增加2.6倍. ...
Comparison of hollow fiber module designs in membrane distillation process employed lumen-side and shell-side feed
1
2015
... 在进料流道中添加间隔物或垫片可以造成小规模涡流,促进反应器中料液的混合,缓解温度极化现象,从而在低进料流速下,也可显示出相对较高的渗透通量〔32〕.间隔物的存在减小了流道的横截面积,使料液的流速增加,导致ΔT1增大,因此TPC增大,温度极化得到缓解〔33〕.然而,在通过调整进料流态来减轻温度极化的影响时,须注意高流速下料液在反应器中的停留时间将减少,膜表面会形成高压降,这可能导致膜孔湿润和渗透通量下降〔34〕. ...
Simulation study of transfer characteristics for spacer-filled membrane distillation desalination modules
1
2017
... 在进料流道中添加间隔物或垫片可以造成小规模涡流,促进反应器中料液的混合,缓解温度极化现象,从而在低进料流速下,也可显示出相对较高的渗透通量〔32〕.间隔物的存在减小了流道的横截面积,使料液的流速增加,导致ΔT1增大,因此TPC增大,温度极化得到缓解〔33〕.然而,在通过调整进料流态来减轻温度极化的影响时,须注意高流速下料液在反应器中的停留时间将减少,膜表面会形成高压降,这可能导致膜孔湿润和渗透通量下降〔34〕. ...
吸收膜蒸馏的传热传质过程
1
2014
... 在进料流道中添加间隔物或垫片可以造成小规模涡流,促进反应器中料液的混合,缓解温度极化现象,从而在低进料流速下,也可显示出相对较高的渗透通量〔32〕.间隔物的存在减小了流道的横截面积,使料液的流速增加,导致ΔT1增大,因此TPC增大,温度极化得到缓解〔33〕.然而,在通过调整进料流态来减轻温度极化的影响时,须注意高流速下料液在反应器中的停留时间将减少,膜表面会形成高压降,这可能导致膜孔湿润和渗透通量下降〔34〕. ...
Flashed-feed VMD configuration as a novel method for eliminating temperature polarization effect and enhancing water vapor flux
1
2018
... 将传统MD工艺进行优化后,对减轻温度极化,提高渗透通量有促进作用.A. S. Alsaadi等〔35〕设计了一种新型的闪蒸进料VMD,进料液在接触疏水膜表面之前被闪蒸,使进料液直接汽化,进料液不与疏水膜直接接触,因此可以极大缓解温度极化.此实验中TPC保持在0.9~0.97,当进料温度分别为60、70、80 ℃时,闪蒸进料VMD工艺的渗透通量相比于传统VMD分别提高了140%、53%、188%.田瑞等〔36〕在AGMD中应用旋转切向入流的方式来减小温度边界层,使近膜面处温度提升,组件的渗透通量提高了30%. ...
太阳能光热-光电膜蒸馏系统发展历程
1
2020
... 将传统MD工艺进行优化后,对减轻温度极化,提高渗透通量有促进作用.A. S. Alsaadi等〔35〕设计了一种新型的闪蒸进料VMD,进料液在接触疏水膜表面之前被闪蒸,使进料液直接汽化,进料液不与疏水膜直接接触,因此可以极大缓解温度极化.此实验中TPC保持在0.9~0.97,当进料温度分别为60、70、80 ℃时,闪蒸进料VMD工艺的渗透通量相比于传统VMD分别提高了140%、53%、188%.田瑞等〔36〕在AGMD中应用旋转切向入流的方式来减小温度边界层,使近膜面处温度提升,组件的渗透通量提高了30%. ...
Study on the heat and mass transfer in air-bubbling enhanced vacuum membrane distillation
1
2015
... Chunrui Wu等〔37〕设计了鼓气VMD,通过向膜组件中鼓入压缩空气促使热料液中形成气液两相流,其可产生较大的扰动和较高的剪切力作用于膜表面,从而减小了边界层的厚度.通过模拟得出鼓气VMD的TPC最高可到0.96,相比传统VMD提高了8%.胡俊虎等〔38〕研究了间歇鼓气VMD,边界层经过周期的扰动状态和稳定状态,有利于渗透通量的提高,当鼓气时间为60 s,鼓气间隔为90 s时渗透通量比持续鼓气时提高了45%. ...
鼓气强化膜蒸馏实验研究
1
2019
... Chunrui Wu等〔37〕设计了鼓气VMD,通过向膜组件中鼓入压缩空气促使热料液中形成气液两相流,其可产生较大的扰动和较高的剪切力作用于膜表面,从而减小了边界层的厚度.通过模拟得出鼓气VMD的TPC最高可到0.96,相比传统VMD提高了8%.胡俊虎等〔38〕研究了间歇鼓气VMD,边界层经过周期的扰动状态和稳定状态,有利于渗透通量的提高,当鼓气时间为60 s,鼓气间隔为90 s时渗透通量比持续鼓气时提高了45%. ...
An electro-thermal braid-reinforced PVDF hollow fiber membrane for vacuum membrane distillation
1
2019
... 新型光热、电热材料的应用,使得膜表面加热成为可能.若利用高温的膜继续对料液加热,则可增大跨膜驱动力,缓解温度极化,提高渗透通量.比如,将镍铬电阻丝编入聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)中空纤维膜中进行MD实验,施加直流电后,膜表面温度可由室温升高到70 ℃,渗透通量提高了2.5倍〔39〕.将银纳米颗粒(Ag-NPs)掺入PVDF膜中,利用其热等离子体特性,可通过紫外辐射提高膜表面温度,在Ag-NPs质量分数为25%时,渗透通量可提高9倍〔40〕. ...
Photothermal membrane distillation for seawater desalination
1
2017
... 新型光热、电热材料的应用,使得膜表面加热成为可能.若利用高温的膜继续对料液加热,则可增大跨膜驱动力,缓解温度极化,提高渗透通量.比如,将镍铬电阻丝编入聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)中空纤维膜中进行MD实验,施加直流电后,膜表面温度可由室温升高到70 ℃,渗透通量提高了2.5倍〔39〕.将银纳米颗粒(Ag-NPs)掺入PVDF膜中,利用其热等离子体特性,可通过紫外辐射提高膜表面温度,在Ag-NPs质量分数为25%时,渗透通量可提高9倍〔40〕. ...
Nanophotonics-enabled solar membrane distillation for off-grid water purification
1
2017
... 近年来,利用膜表面加热冷进料的研究逐渐增多.比如,在PVDF膜上添加SiO2/Au纳米涂层,利用其优良的光热和局部加热性能将太阳能转化为膜表面的热能,可使渗透通量提高33.0%〔7〕.将纳米炭黑颗粒分散到聚乙烯醇(PVA)溶液中,再电纺到PVDF膜上,形成由负载炭黑的PVA纳米纤维与PVDF疏水膜组成的双层结构,当紫外线或太阳辐射照射到膜表面时就会产生局部加热的效果,进而将热量传递给冷料液.在聚焦太阳光下,使用小规模的膜组件可获得5.4 L/(m2·h)的渗透通量,盐分截留率大于99.5%〔41〕. ...
Frequency-dependent stability of CNT Joule heaters in ionizable media and desalination processes
1
2017
... 向PTFE膜上喷涂导电碳纳米管(CNT)及PVA形成导电复合膜,向其施加100 Hz、20 V的交流电后,CNT对电子流动的阻力可导致电子的动能转化为热能,即产生焦耳热效应.利用焦耳热加热冷料液,从而极大地提高了蒸汽压驱动力并且显著减轻了温度极化〔42〕.对含100 g/L NaCl的高盐水的脱盐率超过99%,单程水回收率最高可达12.3%,远超过传统MD中理论最大单程回收率(温差40 ℃时为6.5%)〔43〕. ...
Direct contact membrane distillation with heat recovery: Thermodynamic insights from module scale modeling
1
2014
... 向PTFE膜上喷涂导电碳纳米管(CNT)及PVA形成导电复合膜,向其施加100 Hz、20 V的交流电后,CNT对电子流动的阻力可导致电子的动能转化为热能,即产生焦耳热效应.利用焦耳热加热冷料液,从而极大地提高了蒸汽压驱动力并且显著减轻了温度极化〔42〕.对含100 g/L NaCl的高盐水的脱盐率超过99%,单程水回收率最高可达12.3%,远超过传统MD中理论最大单程回收率(温差40 ℃时为6.5%)〔43〕. ...
Membrane distillation of high salinity water by induction heated thermally conducting membranes
1
2019
... Kuiling Li等〔9〕利用还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)优良的热导电性能,在PTFE膜表面喷涂RGO,制备出可以实现反焦耳加热的复合膜.在AGMD研究中将复合膜置于气隙侧且不与进料液接触,故可避免因反焦耳加热时水的电解和膜的降解.实验中90.56%的热量可传递给冷料液,温度极化现象得到缓解,同时也减轻了膜孔的润湿现象.A. Anvari等〔44〕将PTFE膜上喷涂氧化铁-碳纳米管,制备出可在高频磁场中感应加热的复合膜.在VMD中应用该复合膜之后,渗透通量提高了5.3倍,能耗降低了83%. ...
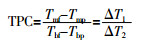
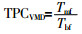
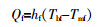
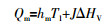
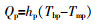
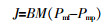



 津公网安备 12010602120337号
津公网安备 12010602120337号