笔者通过RSM优化研究了TiO2/ACF反应器对ARB废水的连续处理过程。首先,在连续循环实验中通过Box-Behnken RSM优化探索该反应器运行参数,考察其连续循环处理效果;其次,在连续循环实验基础上对ARB废水进行连续进出水实验,以期为相关理论与工程应用研究奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂
试剂:ARB由福建某印染厂提供,染料强度为100%。
TiO2/ACF催化剂:采用低温成型法将纳米TiO2负载到活性碳纤维布上自制出实验应用的TiO2/ACF催化剂〔23〕。每10 cm×10 cm活性碳纤维布负载TiO2为171 mg,直径为6~10 nm的纳米TiO2颗粒为32.1%金红石和67.9%锐钛矿的混合物,TiO2/ACF Langmuir比表面积为1 445.71 m2/g、平均孔径为0.67 nm。催化剂投加量按负载TiO2的活性碳纤维布面积计算。
1.2 实验流程
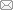
TiO2/ACF反应器降解ARB废水的实验流程见图1。
图1
图1
TiO2/ACF反应器降解ARB废水实验流程
Fig. 1
Experimental process of degradation of ARB wastewater by TiO2/ACF reactor
1.3 实验方法
连续循环实验:单因素实验与RSM优化实验均按连续循环光催化反应流程进行。通过分别改变单次循环时间(30~150 min)、ARB废水质量浓度〔10~50 mg/L(对应色度倍数为100~300倍)〕、TiO2/ACF投加量(40 cm×40 cm~100 cm×100 cm),研究单次循环时间、ARB废水浓度与TiO2/ACF投加量对ARB废水脱色效果的影响,采用RSM优化后的运行参数进行3组平行实验。
连续进出水实验:依据连续循环实验优化结果,考察该反应器连续进出水运行对ARB废水的处理效果。
1.4 表征与分析方法
水样吸光度通过752N紫外-可见分光光度计测定。紫外-可见分光光度计测得ARB废水的最大吸收波长为515 nm。水样吸光度与浓度在515 nm处呈线性关系,根据
式中:C0、Ct ——分别表示水样初始质量浓度和降解后质量浓度,mg/L;
A0、At ——分别为水样初始吸光度和降解后吸光度
η——ARB废水脱色率,%。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 TiO2/ACF反应器运行过程单因素实验结果分析
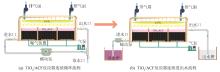
为探索实验各参数适宜范围,将单次循环时间设置变量1~5分别为30、60、90、120、150 min,ARB废水浓度设置变量1~5分别为10、20、30、40、50 mg/L,TiO2/ACF总投加量设置变量1~4分别为40 cm×40 cm、60 cm×60 cm、80 cm×80 cm和100 cm×100 cm分别进行单因素实验,结果见图2。
图2
图2
不同运行条件下ARB废水脱色率对比
Fig. 2
Comparison of decolorization rate of ARB wastewater under different operating conditions
由图2可知,随着单次循环时间增加,ARB废水的脱色率也逐渐增加,单次循环时间在90~150 min范围内ARB废水脱色率较高,循环处理150 min后ARB废水脱色率最大达到82.8%。随着ARB废水初始浓度的提高,ARB废水脱色率整体呈缓慢下降的趋势,其中染料废水质量浓度在20~40 mg/L时脱色率均达到77%以上,质量浓度为20 mg/L时脱色率最大达到83.8%。随着反应器内催化剂总投加量的增加,ARB废水脱色率逐渐增大,投加量为60 cm×60 cm~100 cm×100 cm时废水脱色率均达到80%以上。
综上,当单次循环时间为90~150 min,ARB废水质量浓度为20~40 mg/L,TiO2/ACF催化剂投加量为60 cm×60 cm~100 cm×100 cm时ARB废水脱色率较高。
2.2 Box-Behnken 响应面优化分析与验证
2.2.1 Box-Behnken实验设计
在单因素实验基础上,以单次循环时间(X1)、ARB废水浓度(X2)、催化剂投加量(X3)为自变量,脱色率为响应值,设计三因素三水平Box-Behnken模型进行响应面法优化实验,实验设计见表1。
表1 响应面因素水平编码
Table 1
| 因素 | 代码 | 编码水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 运行时间/min | X1 | 90 | 120 | 150 |
| 质量浓度/(mg·L-1) | X2 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| 投加量/(cm×cm) | X3 | 60×60 | 80×80 | 100×100 |
2.2.2 响应面回归模型可信度分析
表2 脱色率响应面分析实验结果
Table 2
| 序号 | 编码水平 | 去除率/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | 实验值 | 预测值 | |
| 1 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 84.67 | 84.70 |
| 2 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 88.01 | 87.61 |
| 3 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 79.66 | 80.06 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 80.61 | 80.57 |
| 5 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 79.06 | 79.00 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 85.98 | 86.36 |
| 7 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 89.95 | 89.57 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 85.57 | 85.63 |
| 9 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 86.10 | 86.12 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 79.76 | 79.42 |
| 11 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 89.83 | 80.17 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 85.21 | 85.19 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 85.00 | 85.60 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 85.53 | 85.60 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 84.56 | 85.60 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 86.42 | 85.60 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 86.49 | 85.60 |
Y=16.273 17+0.791 64X1-0.459 20X2+0.317 36X3-1.996×10-3X1X2-4.709 96×10-3X1X3+2.149X2X3-1.360 24×10-3X12-0.011 393X22+1.913 97×10-3X32 (R2=0.978 5)
采用方差分析(ANOVA)评估二次多项式回归方程模型见表3。
表3 脱色率方差分析结果
Table 3
| 来源 | 平方和 | 自由度 | 均方 | F值 | P值 (Prob>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 170.62 | 9 | 18.96 | 35.32 | <0.000 1 |
| X1 | 5.85 | 1 | 5.85 | 10.90 | 0.013 1 |
| X2 | 68.21 | 1 | 68.21 | 127.09 | <0.000 1 |
| X3 | 48.31 | 1 | 48.31 | 90.01 | <0.000 1 |
| X1X2 | 1.43 | 1 | 1.43 | 2.67 | 0.146 1 |
| X1X3 | 31.94 | 1 | 31.94 | 59.52 | 0.000 1 |
| X2X3 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.74 | 1.38 | 0.279 0 |
| X12 | 6.31 | 1 | 6.31 | 11.76 | 0.011 0 |
| X22 | 5.47 | 1 | 5.47 | 10.18 | 0.015 3 |
| X32 | 2.47 | 1 | 5.47 | 4.60 | 0.069 2 |
| 残差 | 3.76 | 7 | 0.54 | ||
| 失拟项 | 0.86 | 3 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.762 3 |
| 纯误差 | 2.89 | 4 | 0.72 | ||
| 总离差 | 174.38 | 16 |
此外,R2(0.978 5)和Radj2(0.950 8)值表明所建立的模型代表了响应值与自变量之间的实际关系,Radj2-Rpred2=0.950 8-0.894 8=0.056<0.2,变异系数值为0.86%,小于10%,信噪比为19.88,远高于最低信噪比4,这表明模型可信度满足研究要求〔26〕。
2.2.3 响应曲面分析
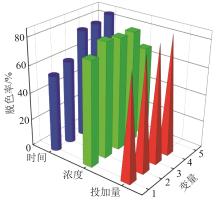
根据单次循环时间(X1)、ARB废水浓度(X2)、催化剂投加量(X3)与脱色率(Y)之间的二次多项回归方程,利用Design Expert Software 8.0.6软件得出响应面和等高线,结果见图3。
图3
图3
单次循环时间、ARB废水浓度、催化剂投加量对ARB废水脱色率影响的响应面和等高线
Fig. 3
Response surface and contour plots of single-cycle time,ARB wastewater concentration,and catalyst dosage on decolorization efficiency of ARB wastewater
根据所建立模型对各实验因子进行优化分析发现,当单次循环时间为103 min,ARB废水初始质量浓度为21 mg/L(对应色度128倍),催化剂投加量为100 cm×100 cm时ARB废水脱色率最高,模型预测值达到90.56%。
2.2.4 响应面优化条件下的验证实验
2.3 ARB废水TiO2/ACF反应器连续进出水脱色过程
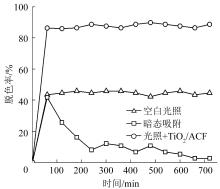
为探究本反应器对ARB废水脱色的持久性以及实用性,以单次循环时间(103 min)为光催化反应器水力停留时间(HRT),ARB废水初始质量浓度(21 mg/L)和催化剂投加量(100 cm×100 cm)不变,进行12 h的连续进出水实验。同时与空白光照(仅高压汞灯光照+曝气)和暗态吸附(仅催化剂吸附+曝气)进行对比,结果见图4。
图4
图4
连续进出水实验3种条件下对ARB废水的脱色效果
Fig. 4
Decolorization effect of ARB dye wastewater under three conditions of continuous inflow and outflow experiment
由图4可知,TiO2/ACF反应器对ARB废水处理可快速达到稳定状态,处理2 h脱色率达到86.29%,持续连续运行10 h后光照+TiO2/ACF条件下对ARB废水脱色率始终稳定在86%左右,色度低于8倍。另外,光照+TiO2/ACF条件下对ARB废水脱色率远大于单一空白光照与暗态吸附条件,空白光照与暗态吸附条件下对ARB废水的脱色率基本在40%以下。这说明TiO2/ACF的吸附-光催化协同作用对ARB废水连续化处理具有明显技术优势。
TiO2/ACF光催化技术与其他处理方法相比具有自身优势,如与张环等〔29〕采用Fe0-PDADMAC/PAA复合膜对ARB废水还原的降解效果(85%)相比,其处理结果基本一致且不存在膜污染问题,刘群等〔30〕采用玉米秸秆/聚苯胺通过间歇、小规模(处理废水0.1 L)吸附处理酸性红B废水,脱色率达到93.4%,虽然脱色效果优于本次实验,但本次研究具有处理规模大(处理废水96 L)且连续运行等优势。此外,同已有光催化连续运行研究结果相比同样具有优势,与Huabing JIANG等〔31〕采用光催化反应器(处理废水3.5 L)对ARB废水连续处理脱色率逐渐降低(结束时<80%)相比,本次研究具有规模大、稳定性高和可持续性强等优势。因此,TiO2/ACF光催化技术在染料废水连续化脱色处理方面具有明显的潜在应用前景。
2.4 降解机理分析
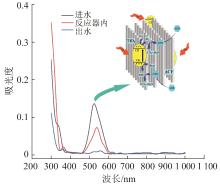
ARB废水进入光催化反应器后,通过TiO2/ACF的吸附-光催化协同作用被脱色降解,降解机理与紫外-可见光光谱图分析见图5。
图5
图5
ARB降解紫外-可见光光谱图和ARB降解机理图
Fig. 5
UV-Vis spectra and mechanism of ARB degradation
由图5还可知,随着反应的进行,酸性红ARB废水在515 nm处吸收峰显著降低且出水吸收峰发生红移,说明ARB染料分子的偶氮键(—N
3 结论
与近年来相关研究报道相比,本研究所采用的TiO2/ACF反应器体积大且为连续运行模式,研究结果表明TiO2/ACF光催化技术在染料废水的连续化脱色处理中具有潜在应用价值,主要研究结论如下:
(1)连续循环实验中,单次循环时间103 min,催化剂投加量100 cm×100 cm的操作条件下,21 mg/L ARB废水的脱色率达到86.43%。
(2)12 h连续进出水实验中,21 mg/L ARB废水2 h时脱色率即达到86.29%,之后始终稳定在86%左右。
参考文献
印染废水深度处理及回用研究进展
[J].
Research progress on deep treatment and recycling of dye wastewater
[J].
印染废水治理技术进展
[J].
Technology progress of dyeing wastewater treatment
[J].
微生物共代谢处理印染废水研究进展
[J].
Research overview of microbial co-metabolism on printing and dyeing wastewater treat-ment
[J].
TiO2光催化剂的研究进展
[J].
Research progress of TiO2 photocatalysts
[J].
Application of titanium dioxide for the photocatalytic degradation of macro- and micro-plastics:A review
[J].
Remediation of noxious pollutants using nano-titania-based photocatalytic construction materials:A review
[J].
PVDF/TiO2电纺纤维膜在光降解和油水分离方面的应用
[J].
Application of PVDF/TiO2 electrospun fiber membrane in photodegradation and oil-water separation
[J].
氧化石墨烯复合二氧化钛光催化剂的制备及模拟染料废水处理
[J].
Preparation of GO/TiO2 composite photocatalyst and treatment of synthetic dye wastewater
[J].
Photocatalytic reactor configurations for water purification:Experimentation and modeling
[J].
Degradation of atenolol in a rectangular staircase photocatalytic reactor with immobilized ZnO
[J].
Photocatalytic water treatment:So where are we going with this?
[J].
Main parameters influencing the design of photocatalytic reactors for wastewater treatment:A mini review
[J].
Synthesis,characterization and advanced sustainable applications of titanium dioxide nanoparticles:A review
[J].
纳米二氧化钛固相载体研究进展
[J].
Research progress of the nano titanium dioxide solid support
[J].
活性碳纤维修饰PbO2电极的制备及其对阿莫西林的降解解毒研究
[J].
Fabrication of PbO2 electrode modified by activated carbon fiber and its degradation and detoxification of amoxicillin
[J].
Photocatalytic application of TiO2-loaded viscose-based activated carbon fibers composite catalyst:Degradation of low concentration formaldehyde and simultaneous anti-microbe
[J].
TiO2/ACF光催化反应器的设计及降解苯酚的研究
[J].
Research on photocatalytic degradation of phenol in waste water using TiO2/ACF and designing photocatalytic reactor
[J].
Recent trends on numerical investigations of response surface methodology for pollutants adsorption onto activated carbon materials:A review
[J].
响应面法优化Fe/TiO2纳米管阵列的制备及其光催化性能研究
[J].
Optimization of the photocatalytic performance for the Fe/TiO2 nanotube arrays by response surface methodology
[J].
A statistical modeling-optimization approach for efficiency photocatalytic degradation of textile azo dye using cerium-doped mesoporous ZnO:A central composite design in response surface methodology
[J].
Response surface methodology and artificial neural network for remediation of acid orange 7 using TiO2-P25:Optimization and modeling approach
[J].
Enhanced selective photocatalytic and sonocatalytic degradation in mixed dye aqueous solution by ZnO/GO nanocomposites:Response surface methodology
[J].
Photocatalytic treatment of RDX wastewater with nano-sized titanium dioxide
[J].
The main role of CuO loading against electron-hole recombination of SrTiO3:Improvement and investigation of photocatalytic activity,modeling and optimization by response surface methodology
[J].
响应曲面优化柏木屑微波活性炭的制备及其吸附AR88性能
[J].
Cypress sawdust based activated carbon preparation and its adsorptive capacity towards macromolecule dye(AR88):Optimization by surface methodology
[J].
Optimizing the acid hydrolysis process for the isolation of microcrystalline cellulose from oil palm empty fruit bunches using response surface methods
[J].
WO3/TiO2薄膜光催化降解ARB性能研究
[J].
Photocatalytic activity of WO3/TiO2 thin film on photocatalytic degradation of ARB
[J].
Degradation of 1,2-dichloroethane by photocatalysis using immobilized PAni-TiO2 nano-photocatalyst
[J].
Fe0-PDADMAC/PAA复合膜还原降解酸性红B
[J].
Reductive degradation of ARB by Fe0-PDADMAC/PAA composite membrane
[J].
玉米秸秆/聚苯胺复合吸附剂对弱酸性红B染料废水的处理
[J].
The study on the adsorption treatment of tracid brilliant red B dye wastewater using polyaniline/maize straw compound adsorbent
[J].
Photocatalytic membrane reactor for degradation of acid red B wastewater
[J].
Synthesis of Ta/Al-Fe2O3 film electrode and its photoelectrocatalytic performance in methylene blue degradation
[J].
Persulfuric acid oxidation mechanism of acid red B wastewater
[J].



 津公网安备 12010602120337号
津公网安备 12010602120337号